Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| (48 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Wang BMCMedInfoDecMak2019 19-1.png|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Design and evaluation of a LIS-based autoverification system for coagulation assays in a core clinical laboratory|Design and evaluation of a LIS-based autoverification system for coagulation assays in a core clinical laboratory]]"''' | ||
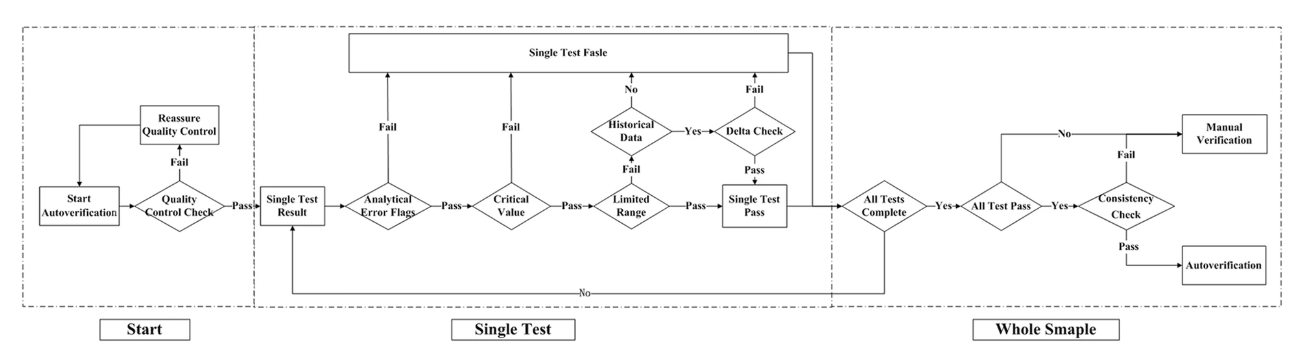
n autoverification system for coagulation consists of a series of rules that allows normal data to be released without manual verification. With new advances in [[medical informatics]], the [[laboratory information system]] (LIS) has growing potential for the use of autoverification, allowing rapid and accurate verification of [[clinical laboratory]] tests. The purpose of the study is to develop and evaluate a LIS-based autoverification system for validation and efficiency. | |||
Autoverification decision rules—including quality control, analytical error flag, critical value, limited range check, delta check, and logical check rules, as well as patient’s historical information—were integrated into the LIS. Autoverification limit ranges was constructed based on 5% and 95% percentiles. The four most commonly used coagulation assays—prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), thrombin time (TT), and fibrinogen (FBG)—were followed by the autoverification protocols. ('''[[Journal:Design and evaluation of a LIS-based autoverification system for coagulation assays in a core clinical laboratory|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal: | : ▪ [[Journal:CyberMaster: An expert system to guide the development of cybersecurity curricula|CyberMaster: An expert system to guide the development of cybersecurity curricula]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal: | : ▪ [[Journal:Costs of mandatory cannabis testing in California|Costs of mandatory cannabis testing in California]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal: | : ▪ [[Journal:An integrated data analytics platform|An integrated data analytics platform]] | ||
Revision as of 15:52, 11 November 2019
n autoverification system for coagulation consists of a series of rules that allows normal data to be released without manual verification. With new advances in medical informatics, the laboratory information system (LIS) has growing potential for the use of autoverification, allowing rapid and accurate verification of clinical laboratory tests. The purpose of the study is to develop and evaluate a LIS-based autoverification system for validation and efficiency.
Autoverification decision rules—including quality control, analytical error flag, critical value, limited range check, delta check, and logical check rules, as well as patient’s historical information—were integrated into the LIS. Autoverification limit ranges was constructed based on 5% and 95% percentiles. The four most commonly used coagulation assays—prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), thrombin time (TT), and fibrinogen (FBG)—were followed by the autoverification protocols. (Full article...)
Recently featured: