Solid-phase microextraction
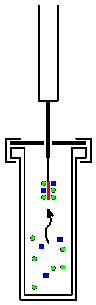
Solid phase microextraction, or SPME, is a solid-phase extraction sampling technique that involves the use of a fiber coated with an extracting phase, that can be a liquid (polymer) or a solid (sorbent),[1] which extracts different kinds of analytes (including both volatile and non-volatile) from different kinds of media, that can be in liquid or gas phase.[2] The quantity of analyte extracted by the fibre is proportional to its concentration in the sample as long as equilibrium is reached or, in case of short time pre-equilibrium, with help of convection or agitation.
Analysis
After extraction, the SPME fiber is transferred to the injection port of separating instruments, such as a gas chromatography and mass spectrometry,[3] where desorption of the analyte takes place and analysis is carried out.
Advantages
The attraction of SPME is that the extraction is fast, simple, can be done usually without solvents, and detection limits can reach parts per trillion (ppt) levels for certain compounds. SPME also has great potential for field applications; on-site sampling can be done even by nonscientists without the need to have gas chromatography-mass spectrometry equipment at each location. When properly stored, samples can be analyzed days later in the laboratory without significant loss of volatiles.[4]
Fiber coatings
The coating on the SPME fiber can be selected to improve sensitivity for specific analytes of interest; ideally the sorbent layer will have a high affinity for the target analytes.[5][6] There are many commercially available SPME fiber coatings that are combinations of polydimethylsiloxane, divinylbenzene, Carboxen, polyacrylate, and polyethylene glycol.[7][8] However, one downside to many of the commercially available SPME fibers is that they tend to be physically brittle due to their composition.[6] Depending on the characteristics of the target analytes, certain properties of the coating improve extraction such as polarity, thickness, and surface area.[5][9] The sample matrix can also influence the fiber coating selection. Based on the sample and analytes of interest, the fiber may need to tolerate direct immersion as opposed to a headspace extraction.[7] In one of the study the fiber coating method significantly enhances the performance of SPME by ensuring a high binding capacity and improved mass transfer efficiency. By preventing the ingress of the polymeric adhesive matrix into the pores of the sorbent particles, the method allows for faster adsorption and desorption times, which is crucial for high-throughput applications.[10]
Application of SPME in forensic science
SPME has become an essential technique in forensic science, particularly for analyzing complex matrices such as blood, urine, and environmental samples. Its advantages include the ability to perform rapid and sensitive extractions without the need for extensive sample preparation, which is crucial in forensic investigations where sample integrity is paramount. For instance, SPME has been successfully employed to detect drugs of abuse, explosives, and other volatile compounds from various samples, allowing for the efficient identification of substances relevant to criminal cases. The automation and miniaturization of SPME techniques further enhance their applicability in forensic settings, enabling high-throughput analysis and reducing the risk of contamination.[4]
Green sample preparation
SPME is recognized as a green analytical method for sample preparation, particularly in forensic drug analysis. This technique offers several advantages over traditional methods like liquid–liquid extraction (LLE) and solid-phase extraction (SPE), including automation, rapid sample processing, and reduced solvent usage. SPME allows for the extraction of analytes directly from complex matrices, such as biological and environmental samples, while minimizing the environmental impact associated with conventional extraction techniques.[4][11]

References
- ^ Spietelun, Agata; Pilarczyk, Michał; Kloskowski, Adam; Namieśnik, Jacek (2010). "Current trends in solid-phase microextraction (SPME) fibre coatings". Chemical Society Reviews. 39 (11): 4524–37. doi:10.1039/c003335a. PMID 20882243.
- ^ Mitra, Somenath, ed. (2003). Sample Preparation Techniques in Analytical Chemistry. p. 113. doi:10.1002/0471457817. ISBN 978-0-471-32845-2.
- ^ Vas, György; Vékey, Károly (2004). "Solid-phase microextraction: a powerful sample preparation tool prior to mass spectrometric analysis". Journal of Mass Spectrometry. 39 (3): 233–254. Bibcode:2004JMSp...39..233V. doi:10.1002/jms.606. PMID 15039931.
- ^ a b c d Verma, Neeraj; Arya, Nikhilesh; Singh, Varoon (2025). "Solid-phase microextraction". Green Analytical Methods and Miniaturized Sample Preparation techniques for Forensic Drug Analysis. pp. 79–112. doi:10.1016/b978-0-443-13907-9.00005-x. ISBN 978-0-443-13907-9.
- ^ a b Spietelun, Agata; Pilarczyk, Michał; Kloskowski, Adam; Namieśnik, Jacek (2010). "Current trends in solid-phase microextraction (SPME) fibre coatings". Chemical Society Reviews. 39 (11): 4524–4537. doi:10.1039/c003335a. PMID 20882243.
- ^ a b Spietelun, Agata; Kloskowski, Adam; Chrzanowski, Wojciech; Namieśnik, Jacek (2012-12-28). "Understanding Solid-Phase Microextraction: Key Factors Influencing the Extraction Process and Trends in Improving the Technique". Chemical Reviews. 113 (3): 1667–1685. doi:10.1021/cr300148j. PMID 23273266.
- ^ a b Reyes-Garcés, Nathaly; Gionfriddo, Emanuela; Gómez-Ríos, German Augusto; Alam, Md. Nazmul; Boyacı, Ezel; Bojko, Barbara; Singh, Varoon; Grandy, Jonathan; Pawliszyn, Janusz (2017-12-14). "Advances in Solid Phase Microextraction and Perspective on Future Directions". Analytical Chemistry. 90 (1): 302–360. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.7b04502. hdl:11511/34478. PMID 29116756.
- ^ Kumar, Ashwini; Gaurav; Malik, Ashok Kumar; Tewary, Dhananjay Kumar; Singh, Baldev (2008-03-03). "A review on development of solid phase microextraction fibers by sol–gel methods and their applications". Analytica Chimica Acta. 610 (1): 1–14. Bibcode:2008AcAC..610....1K. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2008.01.028. PMID 18267134.
- ^ Wardencki, Waldemar; Michulec, Magdalena; Curyło, Janusz (August 2004). "A review of theoretical and practical aspects of solid‐phase microextraction in food analysis". International Journal of Food Science & Technology. 39 (7): 703–717. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.2004.00839.x.
- ^ US20200261887A1, Wirth, Hans-Jürgen & Verma, Neeraj, "Improvements in Solid Phase Micro-Extraction Substrate Coatings", issued 2020-08-20
- ^ López-Lorente, Ángela I.; Pena-Pereira, Francisco; Pedersen-Bjergaard, Stig; Zuin, Vânia G.; Ozkan, Sibel A.; Psillakis, Elefteria (March 2022). "The ten principles of green sample preparation". TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry. 148 116530. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2022.116530. hdl:10852/100181.
Further reading
- Green Analytical Methods and Miniaturized Sample Preparation techniques for Forensic Drug Analysis. 2025. doi:10.1016/C2022-0-02711-2. ISBN 978-0-443-13907-9.
- Janusz Pawliszyn: Handbook of Solid Phase Microextraction, Chemical Industry Press, 2009.
- Pawliszyn J.: Solid Phase Microextraction: Theory and Practice, Wiley-VCH, 1997.
- Pawliszyn J.: Applications of Solid Phase Microextraction, Royal Society of Chemistry, 1999.
Interactive lectures
Notes
This article is a direct transclusion of the Wikipedia article and therefore may not meet the same editing standards as LIMSwiki.









