Instruments used in general medicine
From LIMSWiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2024) |
| Instrument | Uses |
|---|---|
| Bandage | material used to support a medical dressing or injured body part |
| Bedpan | for patients who are unconscious or too weak to sit up or walk to the toilet to defecate |
| Cannula | to create a permanent pathway to a vein (or artery) for the purpose of repeated injections or infusion of intravenous fluids |
| Catheter | to drain and collect urine directly from the bladder (primary use) also to act as a makeshift oxygen tube etc. |
| Crocodile forceps | to remove foreign bodies from ear or nasal cavities. |
| Electrocardiograph machine | to record the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time[1] |
| Enema equipment | to inject fluid into the lower bowel for several purposes, most frequently for relieving constipation |
| Endoscope | to look inside the gastrointestinal tract, used mainly in surgery or by surgical consultants |
| External cardioverter / Defibrillator | to correct arrhythmias of the heart[2] |
| Gas cylinder | as a supply of oxygen, nitrous oxide, carbon dioxide, etc. |
| Gauze sponge | to absorb blood and other fluids as well as clean wounds |
| Glucose monitor | to measure concentration of glucose in blood |
| Haemodialysis machine | to remove toxic materials from the blood that are generally removed by the kidneys; used in case of kidney failure[3] |
| Hypodermic needle / Syringe | for injections and aspiration of blood or fluid from the body |
| Infection control equipment | as in gloves, gowns, bonnets, shoe covers, face shields, goggles, and surgical masks for preventing nosocomial or healthcare-associated infection |
| Instrument sterilizer | to sterilize instruments in absence of an autoclave |
| Kidney dish | as a tray for instruments, gauze, tissue, etc. |
| Measuring tape | for length, height, head circumference and girth measurements |
| Medical halogen penlight | to see into the eye, natural orifices, etc. and to test for pupillary light reflex, etc. |
| Medical ultrasound | to create an image of internal body structures |
| Nasogastric tube | for nasogastric suction or the introduction of food or drugs into the body |
| Nebulizer | to produce aerosols of drugs to be administered by respiratory route |
| Ophthalmoscope | to look at the retina |
| Otoscope | to look into the external ear cavity |
| Oxygen mask and tubes | to deliver gases to the mouth/nostrils to assist in oxygen intake or to administer aerosolized or gaseous drugs |
| Pipette or dropper | to measure out doses of liquid, specially in children |
| Proctoscope | to look inside the anal canal and lower part of the rectum |
| Radiography | to view internal body structures |
| Reflex hammer | to test motor reflexes of the body |
| Sphygmomanometer | to measure the patient's blood pressure |
| Stethoscope | to hear sounds from movements within the body like heart beats, intestinal movement, breath sounds, etc. |
| Suction device | to suck up blood or secretions |
| Surgical scissors | used for dissecting or cutting |
| Thermometer | to record body temperature |
| Tongue depressor | for use in oral examination |
| Transfusion kit | to transfuse blood and blood products |
| Tuning fork | to test for deafness and to categorize it |
| Ventilator | to assist or carry out the mechanical act of inspiration and expiration so the non-respiring patient can do so; a common component of "life support" |
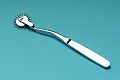
| Wartenberg wheel | for neurological use |
| Watch / Stopwatch | for recording rates like heart rate, respiratory rate, etc.; for certain hearing tests. |
| Weighing scale | to measure weight |
Image gallery
-
Bandage
-
Bedpan
-
Blood infusion set
-
Cannula, intraveneous (separated)
-
Catheter, Foley
-
Defibrillator
-
Dialyser, hemodialysis
-
Enema bag and enema bucket
-
Enema bulb
-
Enema set
-
Endoscope
-
Face shield
-
Gas cylinder, oxygen
-
Gauze sponges
-
Instrument sterilizer
-
Kidney dish
-
Medical halogen penlight
-
Nasogastric tube, Levin
-
Nebulizer
-
Ophthalmoscope
-
Reflex hammer
-
Reflex hammer, queen square
-
Sphygmomanometer, electronic
-
Stethoscope
-
Syringe and needle
-
Thermometers, mercury
-
Tongue depressors
-
Tuning fork
-
Ventilator, high-frequency
-
Weighing scale
-
Wartenberg wheel
Notes
- ^ Khandpur 2020, pp. 563–571.
- ^ Khandpur 2020, pp. 497–501.
- ^ Khandpur 2020, pp. 742–749.
References
- Khandpur, RS (2020). Compendium of Biomedical Instrumentation. United Kingdom: Wiley. ISBN 9781119288121. Retrieved 19 February 2024.
Notes
This article is a direct transclusion of the Wikipedia article and therefore may not meet the same editing standards as LIMSwiki.