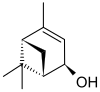
Verbenol
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4,6,6-Trimethylbicyclo[3.1.1]hept-3-en-2-ol | |||
| Other names
2-Pine-4-ol
Pin-2-en-4-ol | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.793 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C10H16O | |||
| Molar mass | 152.237 g·mol−1 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Verbenol (2-pine-4-ol) is a group of stereoisomeric bicyclic monoterpene alcohols. These compounds have been found to be active components of insect pheromones and essential oils.
Isomers
Four stereoisomers of verbenol are known. For the cis isomer, the two methyl groups (-CH3) are on the same side of the carbon ring as the hydroxy group (-OH), and for the trans isomer, they are on the opposite sides. Again, there are enantiomers of each form that exhibit optical activity, that is, turn the plane of linearly polarized light as it passes through the substance or its solution. trans-Verbenol is a mountain pine beetle pheromone that attracts insects to a tree.[1] cis-Verbenol is an aggregation pheromone of Ips typographus[2] and Dendroctonus ponderosae Hopkins.[3]
Enantiomeric composition
Typically, verbenol and related cyclic monoterpenes are available as non‐racemic mixtures of their enantiomers.[4] There are methods to increase enantiomeric excess (optical purity) of verbenol and to isolate individual enantiomers.[5][6]
References
- ^ "New pheromone insight may help predict mountain pine beetle outbreaks". Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^ Jakus, R.; Blazenec, M. (2002). "Influence of proportion of (4S)-cis-verbenol in pheromone bait on Ips typographus (Col., Scolytidae) catch in pheromone trap barrier and in single traps". Journal of Applied Entomology. 126 (6): 306–311. doi:10.1046/j.1439-0418.2002.00659.x. S2CID 83484064.
- ^ Miller, Daniel R. (1991). "Cis-Verbenol: An aggregation pheromone for the mountain pine beetle, Dendroctonus ponderosae Hopkins (Coleoptera: Scolytidae)". J. Entomol. Soc. Brit. Columbia 88: 34-38.
- ^ Gambliel, H.; Croteau, R. (1984). "Pinene cyclases I and II. Two enzymes from sage (Salvia officinalis) which catalyze stereospecific cyclizations of geranyl pyrophosphate to monoterpene olefins of opposite configuration". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 259 (2): 740–748. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(17)43520-4. PMID 6693393.
- ^ Kovalenko, Vitaly et al. Practical method for increasing optical purity of cis‐verbenol. https://doi.org/10.1002/chir.23119
- ^ Mori, Kenji et al. Synthesis of Optically Pure (1S, 4S, 5S)-2-Pinen-4-ol (cis-Verbenol) and Its Antipode, the Pheromone of Ips Bark Beetles. https://doi.org/10.1080/00021369.1976.10862248
Notes
This article is a direct transclusion of the Wikipedia article and therefore may not meet the same editing standards as LIMSwiki.