Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated for the week.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| (492 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Tomich Sustain23 15-8.png|260px]]</div> | ||
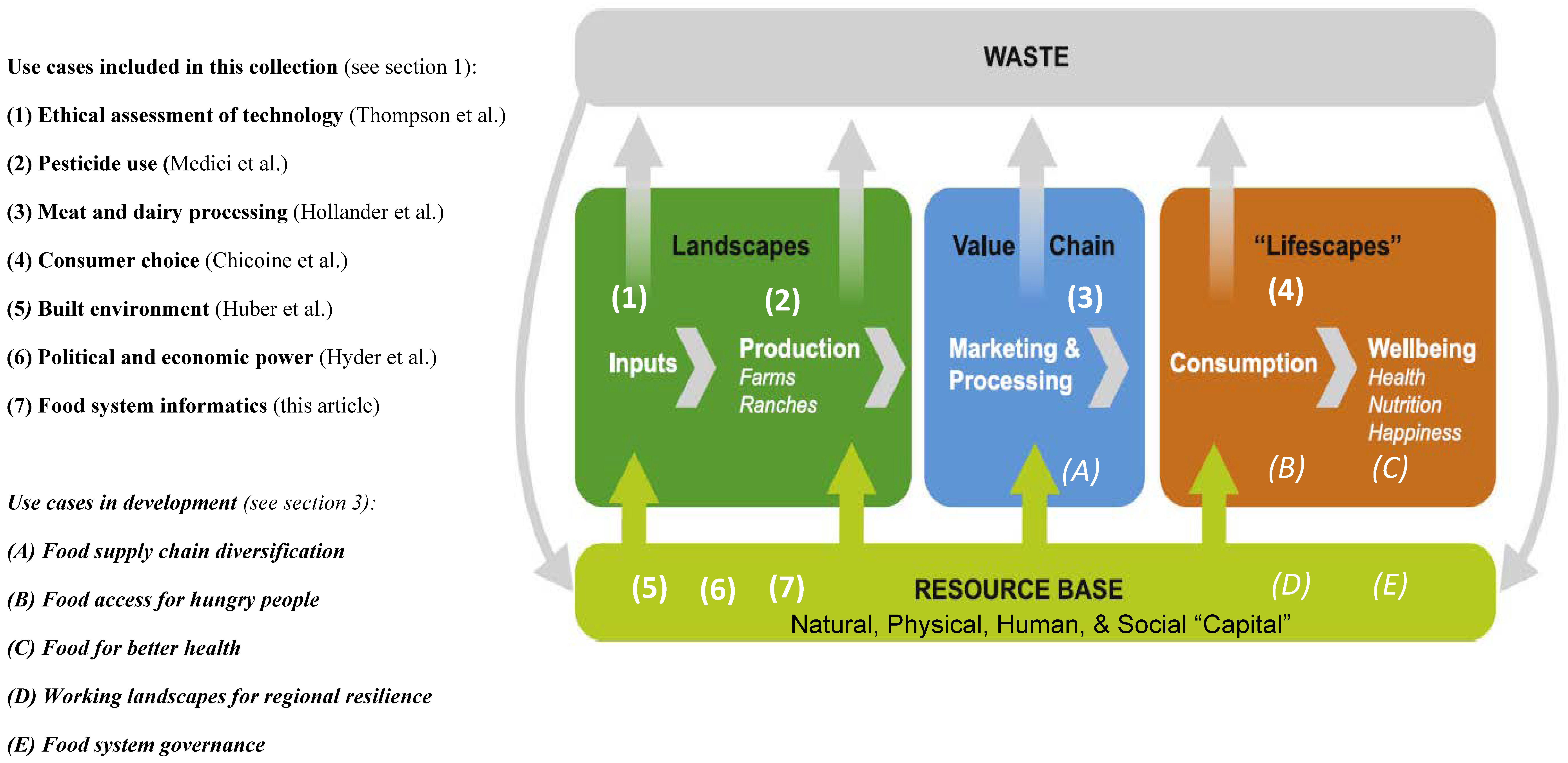
'''[[ | '''"[[Journal:Why do we need food systems informatics? Introduction to this special collection on smart and connected regional food systems|Why do we need food systems informatics? Introduction to this special collection on smart and connected regional food systems]]"''' | ||
Public interest in where food comes from and how it is produced, processed, and distributed has increased over the last few decades, with even greater focus emerging during the [[COVID-19]] [[pandemic]]. Mounting evidence and experience point to disturbing weaknesses in our food systems’ abilities to support human livelihoods and wellbeing, and alarming long-term trends regarding both the environmental footprint of food systems and mounting vulnerabilities to shocks and stressors. How can we tackle the “wicked problems” embedded in a food system? More specifically, how can convergent research programs be designed and resulting knowledge implemented to increase inclusion, sustainability, and resilience within these complex systems ... ('''[[Journal:Why do we need food systems informatics? Introduction to this special collection on smart and connected regional food systems|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
''Recently featured'': | |||
{{flowlist | | |||
<br /> | * [[Journal:Data management challenges for artificial intelligence in plant and agricultural research|Data management challenges for artificial intelligence in plant and agricultural research]] | ||
''Recently featured'': [[ | * [[Journal:A blockchain-driven IoT-based food quality traceability system for dairy products using a deep learning model|A blockchain-driven IoT-based food quality traceability system for dairy products using a deep learning model]] | ||
* [[Journal:Effect of good clinical laboratory practices (GCLP) quality training on knowledge, attitude, and practice among laboratory professionals: Quasi-experimental study|Effect of good clinical laboratory practices (GCLP) quality training on knowledge, attitude, and practice among laboratory professionals: Quasi-experimental study]] | |||
}} | |||
Revision as of 17:11, 22 April 2024
Public interest in where food comes from and how it is produced, processed, and distributed has increased over the last few decades, with even greater focus emerging during the COVID-19 pandemic. Mounting evidence and experience point to disturbing weaknesses in our food systems’ abilities to support human livelihoods and wellbeing, and alarming long-term trends regarding both the environmental footprint of food systems and mounting vulnerabilities to shocks and stressors. How can we tackle the “wicked problems” embedded in a food system? More specifically, how can convergent research programs be designed and resulting knowledge implemented to increase inclusion, sustainability, and resilience within these complex systems ... (Full article...)
Recently featured:
- Data management challenges for artificial intelligence in plant and agricultural research
- A blockchain-driven IoT-based food quality traceability system for dairy products using a deep learning model
- Effect of good clinical laboratory practices (GCLP) quality training on knowledge, attitude, and practice among laboratory professionals: Quasi-experimental study