Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Kohn LearnHlthSys2022 6-1.jpg|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[ | '''"[[Journal:Creating learning health systems and the emerging role of biomedical informatics|Creating learning health systems and the emerging role of biomedical informatics]]"''' | ||
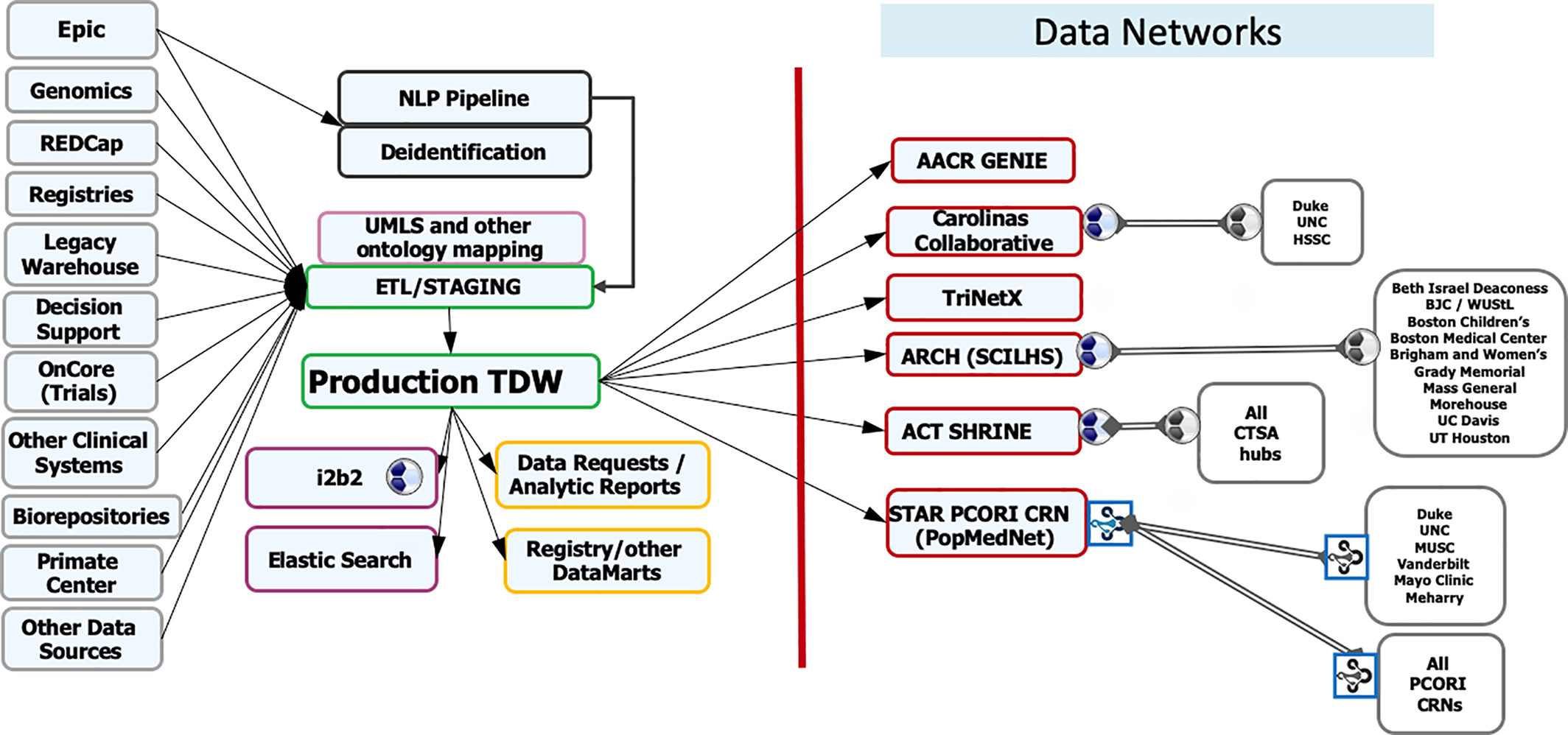
The nature of [[information]] used in medicine has changed. In the past, we were limited to routine clinical data and published clinical trials. Today, we deal with massive, multiple data streams and easy access to new tests, ideas, and capabilities to process them. Whereas in the past getting information for decision-making was a challenge, today's clinicians have readily available access to information and data through the multitude of data-collecting devices, though it remains a challenge at times to analyze, evaluate, and prioritize it. As such, clinicians must become adept with the tools needed to deal with the era of big data, requiring a major change in how we learn to make decisions. Major change is often met with resistance and questions about value. A "learning health system" (LHS) is an enabler to encourage the development of such tools and demonstrate value in improved decision-making ... ('''[[Journal:Creating learning health systems and the emerging role of biomedical informatics|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
{{flowlist | | {{flowlist | | ||
* [[Journal:Planning for Disruptions in Laboratory Operations|Planning for Disruptions in Laboratory Operations]] | |||
* [[Journal:The current state of knowledge on imaging informatics: A survey among Spanish radiologists|The current state of knowledge on imaging informatics: A survey among Spanish radiologists]] | * [[Journal:The current state of knowledge on imaging informatics: A survey among Spanish radiologists|The current state of knowledge on imaging informatics: A survey among Spanish radiologists]] | ||
* [[Journal:Emerging cybersecurity threats in radiation oncology|Emerging cybersecurity threats in radiation oncology]] | * [[Journal:Emerging cybersecurity threats in radiation oncology|Emerging cybersecurity threats in radiation oncology]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 16:16, 17 October 2022
"Creating learning health systems and the emerging role of biomedical informatics"
The nature of information used in medicine has changed. In the past, we were limited to routine clinical data and published clinical trials. Today, we deal with massive, multiple data streams and easy access to new tests, ideas, and capabilities to process them. Whereas in the past getting information for decision-making was a challenge, today's clinicians have readily available access to information and data through the multitude of data-collecting devices, though it remains a challenge at times to analyze, evaluate, and prioritize it. As such, clinicians must become adept with the tools needed to deal with the era of big data, requiring a major change in how we learn to make decisions. Major change is often met with resistance and questions about value. A "learning health system" (LHS) is an enabler to encourage the development of such tools and demonstrate value in improved decision-making ... (Full article...)
Recently featured: