Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Yeste AdvLabMed2021 2-3.jpg|240px]]</div> | ||
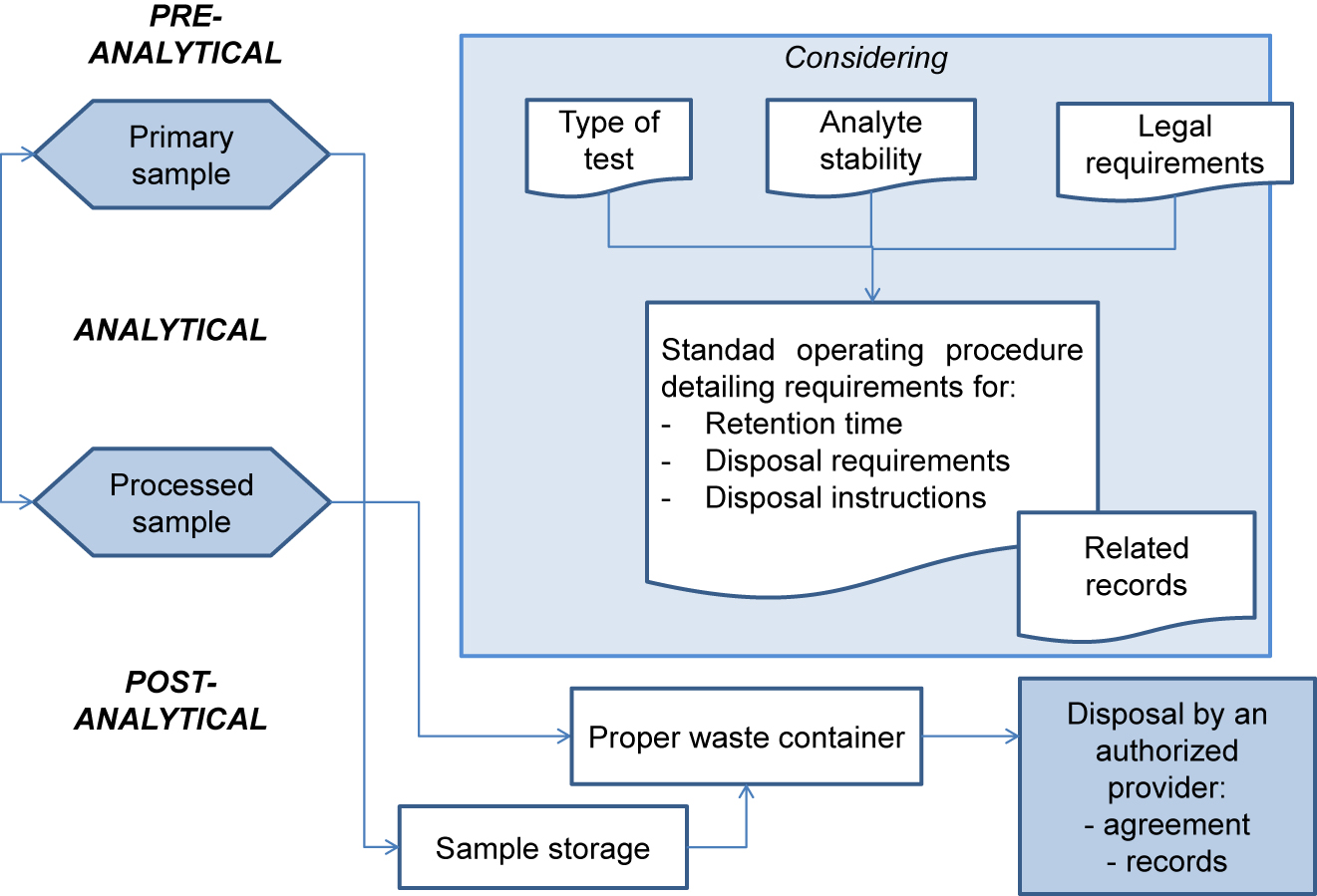
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Management of post-analytical processes in the clinical laboratory according to ISO 15189:2012: Considerations about the management of clinical samples, ensuring quality of post-analytical processes and laboratory information management|Management of post-analytical processes in the clinical laboratory according to ISO 15189:2012: Considerations about the management of clinical samples, ensuring quality of post-analytical processes and laboratory information management]]"''' | ||
[[ | [[ISO 15189|ISO 15189:2012 ''Medical laboratories — Requirements for quality and competence'']] establishes the requirements for clinical specimen management, ensuring the [[Quality (business)|quality]] of processes and [[laboratory]] [[information management]]. ENAC (Entidad Nacional de Acreditación), the sole accreditation authority in Spain, established the requirements for the authorized use of the ISO 15189 accreditation label in reports issued by accredited laboratories. These recommendations are applicable to the lab's post-analytical processes and the professionals involved. The standard requires laboratories to define and document the duration and conditions of specimen [[Retention period|retention]]. Laboratories are also required to design an internal [[quality control]] scheme to verify whether post-analytical activities attain the expected standards. Information management requirements are also established, and laboratories are required to design a contingency plan to ensure the communication of laboratory results ... ('''[[Journal:Management of post-analytical processes in the clinical laboratory according to ISO 15189:2012: Considerations about the management of clinical samples, ensuring quality of post-analytical processes and laboratory information management|Full article...]]''')<br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
{{flowlist | | {{flowlist | | ||
* [[Journal:A survival guide for the rapid transition to a fully digital workflow: The Caltagirone example|A survival guide for the rapid transition to a fully digital workflow: The Caltagirone example]] | |||
* [[Journal:From biobank and data silos into a data commons: Convergence to support translational medicine|From biobank and data silos into a data commons: Convergence to support translational medicine]] | * [[Journal:From biobank and data silos into a data commons: Convergence to support translational medicine|From biobank and data silos into a data commons: Convergence to support translational medicine]] | ||
* [[Journal:Quality management system implementation in human and animal laboratories|Quality management system implementation in human and animal laboratories]] | * [[Journal:Quality management system implementation in human and animal laboratories|Quality management system implementation in human and animal laboratories]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 21:37, 11 September 2022
ISO 15189:2012 Medical laboratories — Requirements for quality and competence establishes the requirements for clinical specimen management, ensuring the quality of processes and laboratory information management. ENAC (Entidad Nacional de Acreditación), the sole accreditation authority in Spain, established the requirements for the authorized use of the ISO 15189 accreditation label in reports issued by accredited laboratories. These recommendations are applicable to the lab's post-analytical processes and the professionals involved. The standard requires laboratories to define and document the duration and conditions of specimen retention. Laboratories are also required to design an internal quality control scheme to verify whether post-analytical activities attain the expected standards. Information management requirements are also established, and laboratories are required to design a contingency plan to ensure the communication of laboratory results ... (Full article...)
Recently featured: