Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig2 Gonzalez-Granadillo Sensors21 21-16.png|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Automated cyber and privacy risk management toolkit|Automated cyber and privacy risk management toolkit]]"''' | ||
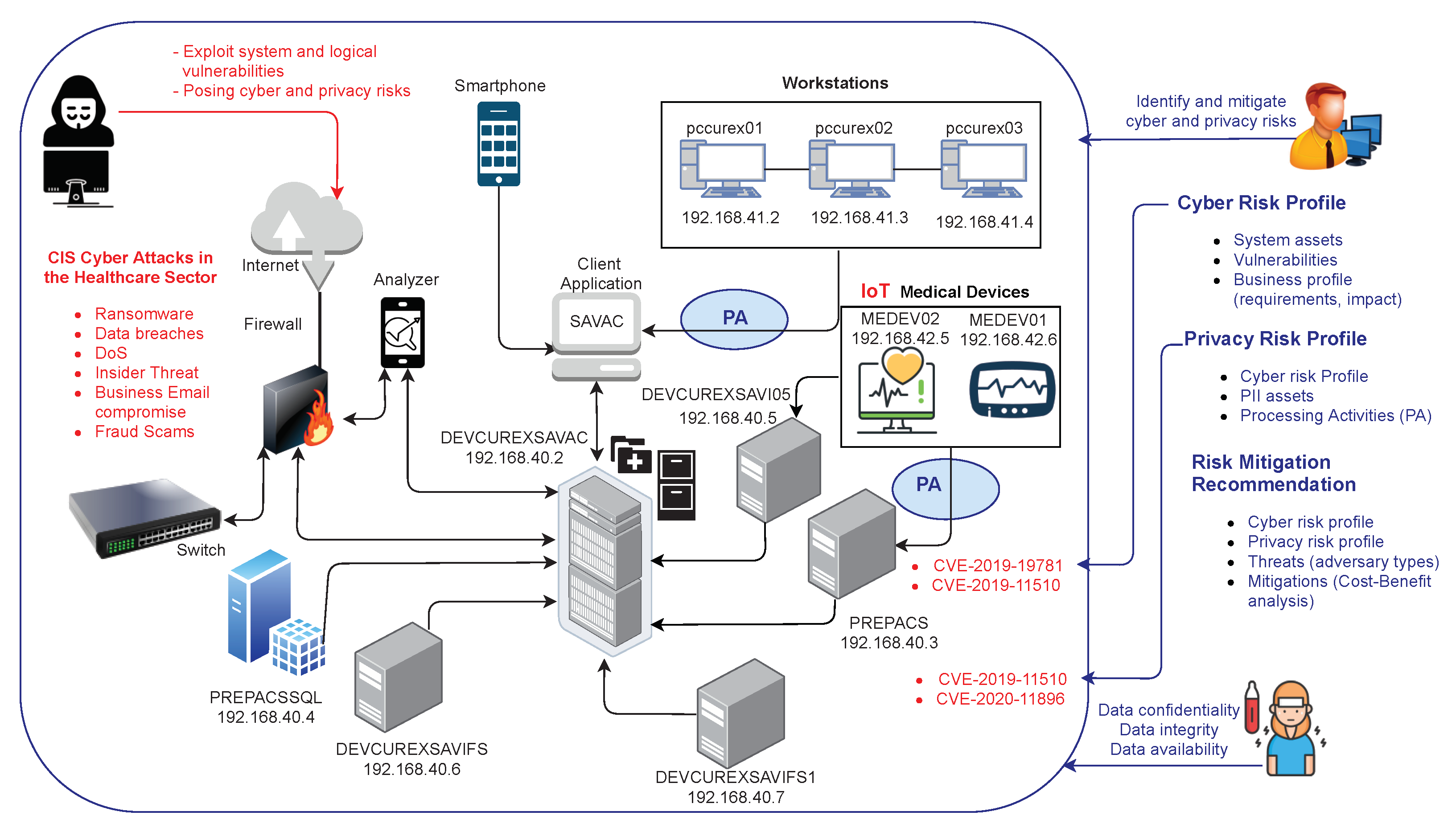
Addressing [[Cybersecurity|cyber]] and [[Information privacy|privacy]] risks has never been more critical for organizations. While a number of [[risk assessment]] methodologies and software tools are available, it is most often the case that one must, at least, integrate them into a holistic approach that combines several appropriate risk sources as input to risk mitigation tools. In addition, cyber risk assessment primarily investigates cyber risks as the consequence of vulnerabilities and threats that threaten assets of the investigated infrastructure. In fact, cyber risk assessment is decoupled from privacy impact assessment, which aims to detect privacy-specific threats and assess the degree of compliance with data protection legislation. Furthermore, a privacy impact assessment (PIA) is conducted in a proactive manner during the design phase of a system, combining processing activities and their inter-dependencies with assets, vulnerabilities, real-time threats and personally identifiable information (PII) that may occur during the dynamic lifecycle of systems. ('''[[Journal:Automated cyber and privacy risk management toolkit|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
{{flowlist | | {{flowlist | | ||
* [[Journal:Design of generalized search interfaces for health informatics|Design of generalized search interfaces for health informatics]] | |||
* [[Journal:Cybersecurity and privacy risk assessment of point-of-care systems in healthcare: A use case approach|Cybersecurity and privacy risk assessment of point-of-care systems in healthcare: A use case approach]] | * [[Journal:Cybersecurity and privacy risk assessment of point-of-care systems in healthcare: A use case approach|Cybersecurity and privacy risk assessment of point-of-care systems in healthcare: A use case approach]] | ||
* [[Journal:Fostering reproducibility, reusability, and technology transfer in health informatics|Fostering reproducibility, reusability, and technology transfer in health informatics]] | * [[Journal:Fostering reproducibility, reusability, and technology transfer in health informatics|Fostering reproducibility, reusability, and technology transfer in health informatics]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 16:31, 7 June 2022
"Automated cyber and privacy risk management toolkit"
Addressing cyber and privacy risks has never been more critical for organizations. While a number of risk assessment methodologies and software tools are available, it is most often the case that one must, at least, integrate them into a holistic approach that combines several appropriate risk sources as input to risk mitigation tools. In addition, cyber risk assessment primarily investigates cyber risks as the consequence of vulnerabilities and threats that threaten assets of the investigated infrastructure. In fact, cyber risk assessment is decoupled from privacy impact assessment, which aims to detect privacy-specific threats and assess the degree of compliance with data protection legislation. Furthermore, a privacy impact assessment (PIA) is conducted in a proactive manner during the design phase of a system, combining processing activities and their inter-dependencies with assets, vulnerabilities, real-time threats and personally identifiable information (PII) that may occur during the dynamic lifecycle of systems. (Full article...)
Recently featured: