Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
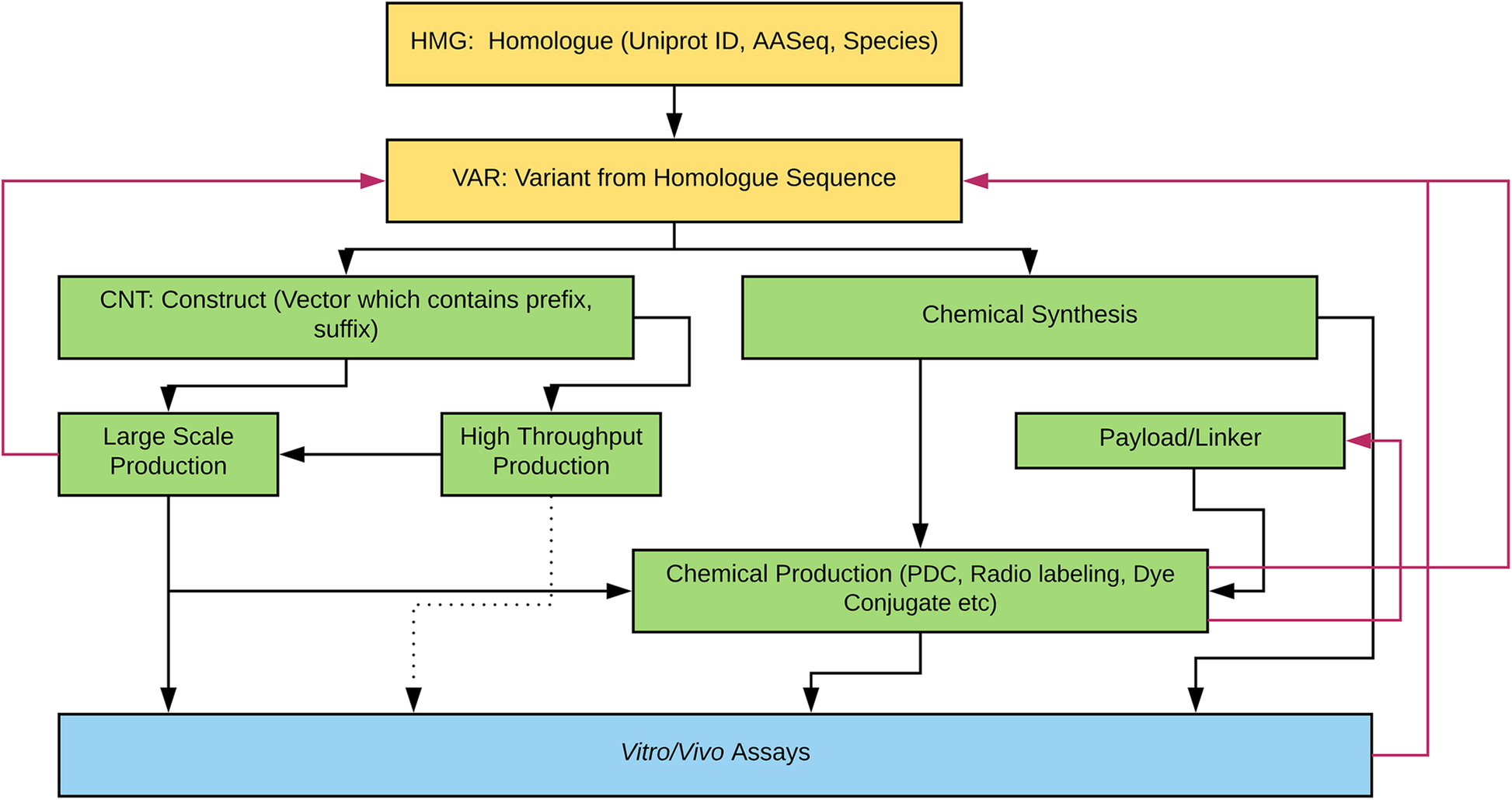
'''"[[Journal: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Brusniak BMCBioinformatics2019 20.png|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal:Laboratory information management software for engineered mini-protein therapeutic workflow|Laboratory information management software for engineered mini-protein therapeutic workflow]]"''' | |||
Protein-based therapeutics are one of the fastest growing classes of novel medical interventions in areas such as cancer, infectious disease, and inflammation. Protein engineering plays an important role in the optimization of desired therapeutic properties such as reducing immunogenicity, increasing stability for storage, increasing target specificity, etc. One category of protein therapeutics is nature-inspired bioengineered cystine-dense peptides (CDPs) for various biological targets. These engineered proteins are often further modified by synthetic chemistry. For example, candidate mini-proteins can be conjugated into active small molecule drugs. We refer to modified mini-proteins as "optides" (optimized peptides). To efficiently serve the multidisciplinary lab scientists with varied therapeutic portfolio research goals in a non-commercial setting, a cost-effective, extendable [[laboratory information management system]] (LIMS) is/was needed. ('''[[Journal:Laboratory information management software for engineered mini-protein therapeutic workflow|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Defending our public biological databases as a global critical infrastructure|Defending our public biological databases as a global critical infrastructure]] | |||
: ▪ [[Journal:Determining the hospital information system (HIS) success rate: Development of a new instrument and case study|Determining the hospital information system (HIS) success rate: Development of a new instrument and case study]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Determining the hospital information system (HIS) success rate: Development of a new instrument and case study|Determining the hospital information system (HIS) success rate: Development of a new instrument and case study]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Smart information systems in cybersecurity: An ethical analysis|Smart information systems in cybersecurity: An ethical analysis]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Smart information systems in cybersecurity: An ethical analysis|Smart information systems in cybersecurity: An ethical analysis]] | ||
Revision as of 16:28, 29 July 2019
"Laboratory information management software for engineered mini-protein therapeutic workflow"
Protein-based therapeutics are one of the fastest growing classes of novel medical interventions in areas such as cancer, infectious disease, and inflammation. Protein engineering plays an important role in the optimization of desired therapeutic properties such as reducing immunogenicity, increasing stability for storage, increasing target specificity, etc. One category of protein therapeutics is nature-inspired bioengineered cystine-dense peptides (CDPs) for various biological targets. These engineered proteins are often further modified by synthetic chemistry. For example, candidate mini-proteins can be conjugated into active small molecule drugs. We refer to modified mini-proteins as "optides" (optimized peptides). To efficiently serve the multidisciplinary lab scientists with varied therapeutic portfolio research goals in a non-commercial setting, a cost-effective, extendable laboratory information management system (LIMS) is/was needed. (Full article...)
Recently featured: