Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| (20 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig4 Ebnehoseini OAccessMacJofMedSci2019 7-9.png|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Determining the hospital information system (HIS) success rate: Development of a new instrument and case study|Determining the hospital information system (HIS) success rate: Development of a new instrument and case study]]"''' | ||
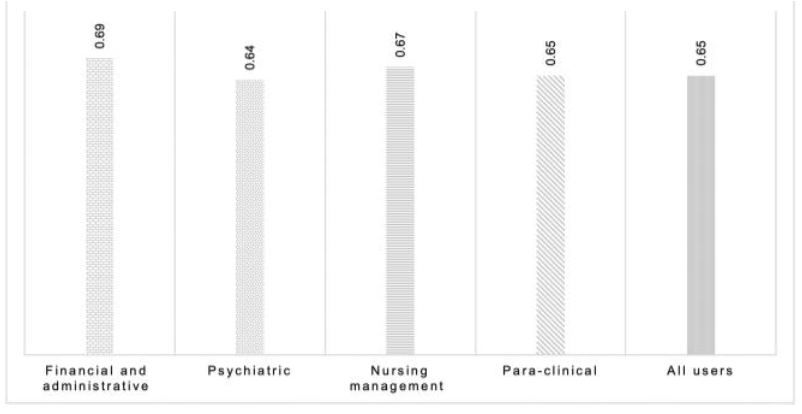
A [[hospital information system]] (HIS) is a type of health information system which is widely used in clinical settings. Determining the success rate of a HIS is an ongoing area of research since its implications are of interest for researchers, physicians, and managers. In the present study, we develop a novel instrument to measure HIS success rate based on users’ viewpoints in a teaching [[hospital]]. The study was conducted in Ibn-e Sina and Dr. Hejazi Psychiatry Hospital and education center in Mashhad, Iran. The instrument for data collection was a self-administered structured questionnaire based on the information systems success model (ISSM), covering seven dimensions, which includes system quality, [[information]] quality, service quality, system use, usefulness, satisfaction, and net benefits. The verification of content validity was carried out by an expert panel. The internal consistency of dimensions was measured by Cronbach’s alpha. Pearson’s correlation coefficient was calculated to evaluate the significance of associations between dimensions. The HIS success rate on users’ viewpoints was determined. ('''[[Journal:Determining the hospital information system (HIS) success rate: Development of a new instrument and case study|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal: | : ▪ [[Journal:Smart information systems in cybersecurity: An ethical analysis|Smart information systems in cybersecurity: An ethical analysis]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal: | : ▪ [[Journal:Chemometric analysis of cannabinoids: Chemotaxonomy and domestication syndrome|Chemometric analysis of cannabinoids: Chemotaxonomy and domestication syndrome]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal: | : ▪ [[Journal:National and transnational security implications of asymmetric access to and use of biological data|National and transnational security implications of asymmetric access to and use of biological data]] | ||
Revision as of 16:04, 15 July 2019
A hospital information system (HIS) is a type of health information system which is widely used in clinical settings. Determining the success rate of a HIS is an ongoing area of research since its implications are of interest for researchers, physicians, and managers. In the present study, we develop a novel instrument to measure HIS success rate based on users’ viewpoints in a teaching hospital. The study was conducted in Ibn-e Sina and Dr. Hejazi Psychiatry Hospital and education center in Mashhad, Iran. The instrument for data collection was a self-administered structured questionnaire based on the information systems success model (ISSM), covering seven dimensions, which includes system quality, information quality, service quality, system use, usefulness, satisfaction, and net benefits. The verification of content validity was carried out by an expert panel. The internal consistency of dimensions was measured by Cronbach’s alpha. Pearson’s correlation coefficient was calculated to evaluate the significance of associations between dimensions. The HIS success rate on users’ viewpoints was determined. (Full article...)
Recently featured: