Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
From LIMSWiki
Jump to navigationJump to searchShawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Malykh JofHealthEng2018 2018.png|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Approaches to medical decision-making based on big clinical data|Approaches to medical decision-making based on big clinical data]]"''' | ||
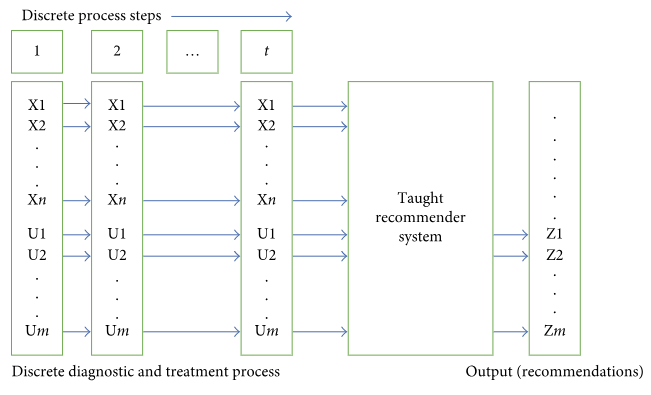
The paper discusses different approaches to building a [[clinical decision support system]] based on big data. The authors sought to abstain from any data reduction and apply universal teaching and big data processing methods independent of disease classification standards. The paper assesses and compares the accuracy of recommendations among three options: case-based reasoning, simple single-layer neural network, and probabilistic neural network. Further, the paper substantiates the assumption regarding the most efficient approach to solving the specified problem. ('''[[Journal:Approaches to medical decision-making based on big clinical data|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:A new numerical method for processing longitudinal data: Clinical applications|A new numerical method for processing longitudinal data: Clinical applications]] | |||
: ▪ [[Journal:Big data management for healthcare systems: Architecture, requirements, and implementation|Big data management for healthcare systems: Architecture, requirements, and implementation]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Big data management for healthcare systems: Architecture, requirements, and implementation|Big data management for healthcare systems: Architecture, requirements, and implementation]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Support Your Data: A research data management guide for researchers|Support Your Data: A research data management guide for researchers]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Support Your Data: A research data management guide for researchers|Support Your Data: A research data management guide for researchers]] | ||
Revision as of 18:58, 17 December 2018
"Approaches to medical decision-making based on big clinical data"
The paper discusses different approaches to building a clinical decision support system based on big data. The authors sought to abstain from any data reduction and apply universal teaching and big data processing methods independent of disease classification standards. The paper assesses and compares the accuracy of recommendations among three options: case-based reasoning, simple single-layer neural network, and probabilistic neural network. Further, the paper substantiates the assumption regarding the most efficient approach to solving the specified problem. (Full article...)
Recently featured: