Heterocyclic compound


A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a hydrocarbon-based cyclic compound that contains at least one heteroatom as member(s) of its ring(s).[1] Heterocyclic organic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of organic heterocycles.[2]
Examples of heterocyclic compounds include all of the nucleic acids, the majority of drugs, most biomass (cellulose and related materials), and many natural and synthetic dyes. More than half of known compounds are heterocycles.[3] 59% of US FDA-approved drugs contain nitrogen heterocycles.[4]
Classification
The study of organic heterocyclic chemistry focuses especially on organic unsaturated derivatives, and the preponderance of work and applications involves unstrained organic 5- and 6-membered rings. Included are pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan. Another large class of organic heterocycles refers to those fused to benzene rings. For example, the fused benzene derivatives of pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan are quinoline, benzothiophene, indole, and benzofuran, respectively. The fusion of two benzene rings gives rise to a third large family of organic compounds. Analogs of the previously mentioned heterocycles for this third family of compounds are acridine, dibenzothiophene, carbazole, and dibenzofuran, respectively.
Heterocyclic organic compounds can be usefully classified based on their electronic structure. The saturated organic heterocycles behave like the acyclic derivatives. Thus, piperidine and tetrahydrofuran are conventional amines and ethers, with modified steric profiles. Therefore, the study of organic heterocyclic chemistry focuses on organic unsaturated rings.
Inorganic rings
Some heterocycles contain no carbon. Examples are borazine (B3N3 ring), hexachlorophosphazene (P3N3 ring), and trithiazyl trichloride (S3N3 ring). In comparison with organic heterocycles, which have numerous commercial applications, inorganic ring systems are mainly of theoretical interest. IUPAC recommends the Hantzsch-Widman nomenclature for naming heterocyclic compounds.[5]
Notes on lists
- "Heteroatoms" are atoms in the ring other than carbon atoms.
- Names in italics are retained by IUPAC and do not follow the Hantzsch-Widman nomenclature.
- Some of the names refer to classes of compounds rather than individual compounds.
- Also no attempt is made to list isomers.
3-membered rings
Although subject to ring strain, 3-membered heterocyclic rings are well characterized.[6]
| Three-membered rings with one heteroatom | ||
|---|---|---|
| Heteroatom | Saturated | Unsaturated |
| Boron | Borirane | Borirene |
| Nitrogen | Aziridine | Azirine |
| Oxygen | Oxirane (ethylene oxide, epoxides) |
Oxirene |
| Silicon | Silirane | Silirene |
| Phosphorus | Phosphirane | Phosphirene |
| Sulfur | Thiirane (ethylene sulfide, episulfides) |
Thiirene |
| Three-membered rings with two heteroatoms | ||
| Heteroatoms | Saturated | Unsaturated |
| 2 × Nitrogen | Diaziridine | Diazirine |
| Nitrogen + Oxygen | Oxaziridine | Oxazirine |
| Nitrogen + Sulfur | Thiaziridine | Thiazirine |
| 2 × Oxygen | Dioxirane (highly unstable) | - - - - - - |
| 2 × Sulfur | Dithiirane (highly unstable) | - - - - - - |
4-membered rings
| Four-membered rings with one heteroatom | ||
|---|---|---|
| Heteroatom | Saturated | Unsaturated |
| Boron | Boretane | Borete |
| Nitrogen | Azetidine | Azete |
| Oxygen | Oxetane | Oxete |
| Silicon | Siletane | Silete |
| Phosphorus | Phosphetane | Phosphete |
| Sulfur | Thietane | Thiete |
| Four-membered rings with two heteroatoms | ||
| Heteroatoms | Saturated | Unsaturated |
| 2 × Nitrogen | Diazetidine | Diazete |
| 2 × Oxygen | Dioxetane | Dioxete |
| 2 × Sulfur | Dithietane | Dithiete |
5-membered rings
The 5-membered ring compounds containing two heteroatoms, at least one of which is nitrogen, are collectively called the azoles. Thiazoles and isothiazoles contain a sulfur and a nitrogen atom in the ring. Dithioles have two sulfur atoms.
A large group of 5-membered ring compounds with three or more heteroatoms also exists. One example is the class of dithiazoles, which contain two sulfur atoms and one nitrogen atom.
| Five-membered rings with one heteroatom | ||
|---|---|---|
| Heteroatom | Saturated | Unsaturated |
| Boron | Borolane | Borole |
| Nitrogen | Pyrrolidine (Azolidine not used) |
Pyrrole (Azole not used) Pyrroline (partially unsaturated) |
| Oxygen | Oxolane | Furan (Oxole not used) |
| Silicon | Silolane | Silole |
| Phosphorus | Phospholane | Phosphole |
| Sulfur | Thiolane | Thiophene (Thiole not used) |
| Germanium | Germolane | Germole |
| Arsenic | Arsolane | Arsole |
| Selenium | Selenolane | Selenophene |
| Tin | Stannolane | Stannole |
| Antimony | Stibolane | Stibole |
| Tellurium | Tellurolane | Tellurophene |
| Lead | Plumbolane | Plumbole |
| Bismuth | Bismolane | Bismole |
| Five-membered rings with two heteroatoms | ||
| Heteroatoms | Saturated | Unsaturated (and partially unsaturated) |
| 2 × Nitrogen | Pyrazolidine Imidazolidine |
Pyrazole (Pyrazoline) Imidazole (Imidazoline) |
| Nitrogen + Oxygen | Oxazolidine Isoxazolidine |
Oxazole (Oxazoline) Isoxazole (Isoxazoline) |
| Nitrogen + Sulfur | Thiazolidine Isothiazolidine |
Thiazole (Thiazoline) Isothiazole (Isothiazoline) |
| Oxygen + Sulfur | Oxathiolane Isoxathiolane |
Oxathiole Isoxathiole |
| 2 × Oxygen | Dioxolane | Dioxole |
| 2 × Sulfur | Dithiolane | Dithiole |
| Five-membered rings with three heteroatoms | ||
| Heteroatoms | Unsaturated | |
| 3 × Nitrogen | Triazole | |
| 2 Nitrogen + Oxygen | Oxadiazole | |
| 2 Nitrogen + Sulfur | Thiadiazole | |
| Nitrogen + 2 Oxygen | Dioxazole | |
| Nitrogen + 2 Sulfur | Dithiazole | |
| Five-membered rings with four heteroatoms | ||
| Heteroatoms | Unsaturated | |
| 4 × Nitrogen | Tetrazole | |
| 3 Nitrogen + Oxygen | Oxatriazole | |
| 3 Nitrogen + Sulfur | Thiatriazole | |
| Five-membered rings with five heteroatoms | ||
| Heteroatoms | Unsaturated | |
| 5 × Nitrogen | Pentazole | |
| 4 Nitrogen + Oxygen | Oxatetrazole | |
| 4 Nitrogen + Sulfur | Thiatetrazole | |
6-membered rings
The 6-membered ring compounds containing two heteroatoms, at least one of which is nitrogen, are collectively called the azines. Thiazines contain a sulfur and a nitrogen atom in the ring. Dithiines have two sulfur atoms.
| Six-membered rings with one heteroatom | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Heteroatom | Saturated | Unsaturated | Ions |
| Boron | Borinane | Borinine | Boratabenzene anion |
| Nitrogen | Piperidine (Azinane not used) |
Pyridine (Azine not used) |
Pyridinium cation |
| Oxygen | Oxane | Pyran (Oxine not used) |
Pyrylium cation |
| Silicon | Silinane | Siline | - - - - - - |
| Phosphorus | Phosphinane | Phosphinine | Phosphininium cation[7] |
| Sulfur | Thiane | Thiopyran (Thiine not used) |
Thiopyrylium cation |
| Germanium | Germinane | Germine | - - - - - - |
| Arsenic | Arsinane | Arsinine | Arsatabenzene cation |
| Selenium | Selenane | Selenopyran | Selenopyrylium cation |
| Tin | Stanninane | Stannine | - - - - - - |
| Antimony | Stibinane | Stibinine | Stibatabenzene cation |
| Tellurium | Tellurane | Telluropyran | Telluropyrylium cation |
| Lead | Plumbinane | Plumbine | - - - - - - |
| Bismuth | Bisminane | Bismine | Bismatabenzene cation |
| Six-membered rings with two heteroatoms | |||
| Heteroatoms | Saturated | Unsaturated | |
| 2 × Nitrogen | Piperazine | Pyrazine Pyrimidine Pyridazine | |
| Nitrogen + Oxygen | Morpholine | Oxazine | |
| Nitrogen + Sulfur | Thiomorpholine | Thiazine | |
| Oxygen + Sulfur | Oxathiane | Oxathiin | |
| 2 × Oxygen | Dioxane | Dioxin | |
| 2 × Sulfur | Dithiane | Dithiin | |
| Six-membered rings with three heteroatoms | |||
| Heteroatoms | Saturated | Unsaturated | |
| 3 × Nitrogen | Triazinane | Triazine | |
| 3 × Oxygen | Trioxane | Trioxin | |
| 3 × Sulfur | Trithiane | Trithiin | |
| Six-membered rings with four heteroatoms | |||
| Heteroatoms | Unsaturated | ||
| 4 × Nitrogen | Tetrazine | ||
| 2 Nitrogen + 2 Boron | Carborazine | ||
Six-membered rings with five heteroatoms
The hypothetical chemical compound with five nitrogen heteroatoms would be pentazine.
Six-membered rings with six heteroatoms
The hypothetical chemical compound with six nitrogen heteroatoms would be hexazine. Borazine is a six-membered ring with three nitrogen heteroatoms and three boron heteroatoms.
7-membered rings
In a 7-membered ring, the heteroatom must be able to provide an empty π-orbital (e.g. boron) for "normal" aromatic stabilization to be available; otherwise, homoaromaticity may be possible.
| Seven-membered rings with one heteroatom | ||
|---|---|---|
| Heteroatom | Saturated | Unsaturated |
| Boron | Borepane | Borepine |
| Nitrogen | Azepane | Azepine |
| Oxygen | Oxepane | Oxepine |
| Silicon | Silepane | Silepine |
| Phosphorus | Phosphepane | Phosphepine |
| Sulfur | Thiepane | Thiepine |
| Seven-membered rings with two heteroatoms | ||
| Heteroatoms | Saturated | Unsaturated |
| 2 × Nitrogen | Diazepane | Diazepine |
| Nitrogen + Oxygen | Oxazepane | Oxazepine |
| Nitrogen + Sulfur | Thiazepane | Thiazepine |
8-membered rings
| Heteroatom | Saturated | Unsaturated |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | Azocane | Azocine |
| Oxygen | Oxocane | Oxocine |
| Sulfur | Thiocane | Thiocine |
Borazocine is an eight-membered ring with four nitrogen heteroatoms and four boron heteroatoms.
9-membered rings
| Heteroatom | Saturated | Unsaturated |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | Azonane | Azonine |
| Oxygen | Oxonane | Oxonine |
| Sulfur | Thionane | Thionine |
Images of rings with one heteroatom
| Saturated | Unsaturated | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heteroatom | Nitrogen | Oxygen | Sulfur | Nitrogen | Oxygen | Sulfur |
| 3-atom ring | Aziridine | Oxirane | Thiirane | Azirine | Oxirene | Thiirene |
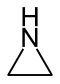 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

| |
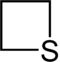
| 4-atom ring | Azetidine | Oxetane | Thietane | Azete | Oxete | Thiete |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

| |
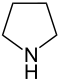
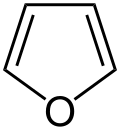
| 5-atom ring | Pyrrolidine | Oxolane | Thiolane | Pyrrole | Furan | Thiophene |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

| |
| 6-atom ring | Piperidine | Oxane | Thiane | Pyridine | Pyran | Thiopyran |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

| |
| 7-atom ring | Azepane | Oxepane | Thiepane | Azepine | Oxepine | Thiepine |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

| |
| 8-atom ring | Azocane | Oxocane | Thiocane | Azocine | Oxocine | Thiocine |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

| |
| 9-atom ring | Azonane | Oxonane | Thionane | Azonine | Oxonine | Thionine |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

| |
Fused/condensed rings
Heterocyclic rings systems that are formally derived by fusion with other rings, either carbocyclic or heterocyclic, have a variety of common and systematic names. For example, with the benzo-fused unsaturated nitrogen heterocycles, pyrrole provides indole or isoindole depending on the orientation. The pyridine derivative is quinoline or isoquinoline, and the class of analogues with two nitrogen atoms is known as the benzodiazines. For the azepine derivative, benzazepine is the preferred name. Likewise, the compounds with two benzene rings fused to the central heterocycle are carbazole, acridine, and dibenzoazepine. Heptazine is a tricyclic nitrogen-containing heterocyclic system derived by fusion of three triazine rings, and analog of the carbocycle phenalene.
History of heterocyclic chemistry
The history of heterocyclic chemistry began in the 1800s, in step with the development of organic chemistry. Some noteworthy developments:[8]
- 1818: Brugnatelli makes alloxan from uric acid.
- 1832: Dobereiner produces furfural (a furan) by treating starch with sulfuric acid.
- 1834: Runge obtains pyrrole ("fiery oil") by dry distillation of bones.
- 1906: Friedlander synthesizes indigo dye, allowing synthetic chemistry to displace a large agricultural industry.
- 1936: Treibs isolates chlorophyll derivatives from crude oil, explaining the biological origin of petroleum.
- 1951: Chargaff's rules are described, highlighting the role of heterocyclic compounds (purines and pyrimidines) in the genetic code.
Uses
Heterocyclic compounds are pervasive in many areas of life sciences and technology.[2] Many drugs are heterocyclic compounds.[9] Among the modifications to the family of antitumor compounds, heterocyclic organic compounds have been extensively applied by many groups in order to modify the reactivity profile. Pyrrole, pyrimidine, indole, quinoline and purine are few classes of heterocycles which showed interesting cytotoxicity profiles, which can be highly beneficial when developing cancer drugs.[10]
See also
References
- ^ IUPAC Gold Book heterocyclic compounds
- ^ a b Thomas L. Gilchrist "Heterocyclic Chemistry" 3rd ed. Addison Wesley: Essex, England, 1997. 414 pp. ISBN 0-582-27843-0.
- ^ Rees, Charles W. (1992). "Polysulfur-Nitrogen Heterocyclic Chemistry". Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry. 29 (3): 639–651. doi:10.1002/jhet.5570290306.
- ^ Edon Vitaku, David T. Smith, Jon T. Njardarson (2014). "Analysis of the Structural Diversity, Substitution Patterns, and Frequency of Nitrogen Heterocycles among U.S. FDA Approved Pharmaceuticals". J. Med. Chem. 57 (24): 10257–10274. doi:10.1021/jm501100b. PMID 25255204.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 5th ed. (the "Gold Book") (2025). Online version: (2006–) "Hantzsch–Widman name". doi:10.1351/goldbook.H02737
- ^ Smith, Michael B.; March, Jerry (2007), Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure (6th ed.), New York: Wiley-Interscience, ISBN 978-0-471-72091-1
- ^ Fischer, Lukas; Wossidlo, Friedrich; Frost, Daniel; Coles, Nathan T.; Steinhauer, Simon; Riedel, Sebastian; Müller, Christian (6 August 2021) [19th July 2021]. "One-step methylation of aromatic phosphorus heterocycles: synthesis and crystallographic characterization of a 1-methyl-phosphininium salt". Chemical Communications. 57 (2021, 57). Royal Society of Chemistry: 9522–9525. doi:10.1039/D1CC03892C. PMID 34546255.
- ^ Campaigne, E. (1986). "Adrien Albert and the rationalization of heterocyclic chemistry". Journal of Chemical Education. 63 (10): 860. Bibcode:1986JChEd..63..860C. doi:10.1021/ed063p860.
- ^ "IPEXL.com Multilingual Patent Search, Patent Ranking". www.ipexl.com. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 8 September 2010.
- ^ Kidwai, M.; Venktaramanan, R.; Mohan, R.; Sapra, P. (1 June 2002). "Cancer Chemotherapy and Heterocyclic Compounds". Current Medicinal Chemistry. 9 (12): 1209–1228. doi:10.2174/0929867023370059. ISSN 0929-8673. PMID 12052173. Archived from the original on 20 June 2024.
External links
- Hantzsch-Widman nomenclature, IUPAC
- Heterocyclic amines in cooked meat, US CDC
- List of known and probable carcinogens, American Cancer Society Archived 13 December 2003 at the Wayback Machine
- List of known carcinogens by the State of California, Proposition 65 (more comprehensive)
Notes
This article is a direct transclusion of the Wikipedia article and therefore may not meet the same editing standards as LIMSwiki.









