|
If you're looking for the 2014 archive, it can be found here. The 2015 archive is here. |
Featured article of the week archive - 2016
Welcome to the LIMSwiki 2016 archive for the Featured Article of the Week.
Featured article of the week: February 15–21:
"SaDA: From sampling to data analysis—An extensible open source infrastructure for rapid, robust and automated management and analysis of modern ecological high-throughput microarray data"
One of the most crucial characteristics of day-to-day laboratory information management is the collection, storage and retrieval of information about research subjects and environmental or biomedical samples. An efficient link between sample data and experimental results is absolutely important for the successful outcome of a collaborative project. Currently available software solutions are largely limited to large scale, expensive commercial Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS). Acquiring such LIMS indeed can bring laboratory information management to a higher level, but most of the times this requires a sufficient investment of money, time and technical efforts. There is a clear need for a light weighted open source system which can easily be managed on local servers and handled by individual researchers. Here we present a software named SaDA for storing, retrieving and analyzing data originated from microorganism monitoring experiments. SaDA is fully integrated in the management of environmental samples, oligonucleotide sequences, microarray data and the subsequent downstream analysis procedures. It is simple and generic software, and can be extended and customized for various environmental and biomedical studies. (Full article...)
Featured article of the week: January 25–31:
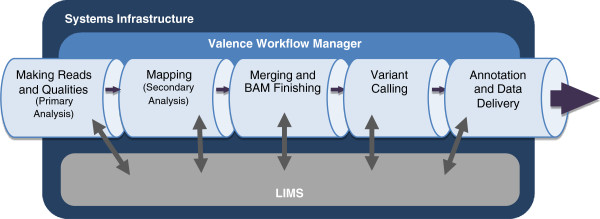
"Launching genomics into the cloud: Deployment of Mercury, a next generation sequence analysis pipeline"
Massively parallel DNA sequencing generates staggering amounts of data. Decreasing cost, increasing throughput, and improved annotation have expanded the diversity of genomics applications in research and clinical practice. This expanding scale creates analytical challenges: accommodating peak compute demand, coordinating secure access for multiple analysts, and sharing validated tools and results.
To address these challenges, we have developed the Mercury analysis pipeline and deployed it in local hardware and the Amazon Web Services cloud via the DNAnexus platform. Mercury is an automated, flexible, and extensible analysis workflow that provides accurate and reproducible genomic results at scales ranging from individuals to large cohorts.
By taking advantage of cloud computing and with Mercury implemented on the DNAnexus platform, we have demonstrated a powerful combination of a robust and fully validated software pipeline and a scalable computational resource that, to date, we have applied to more than 10,000 whole genome and whole exome samples. (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: January 18–24:
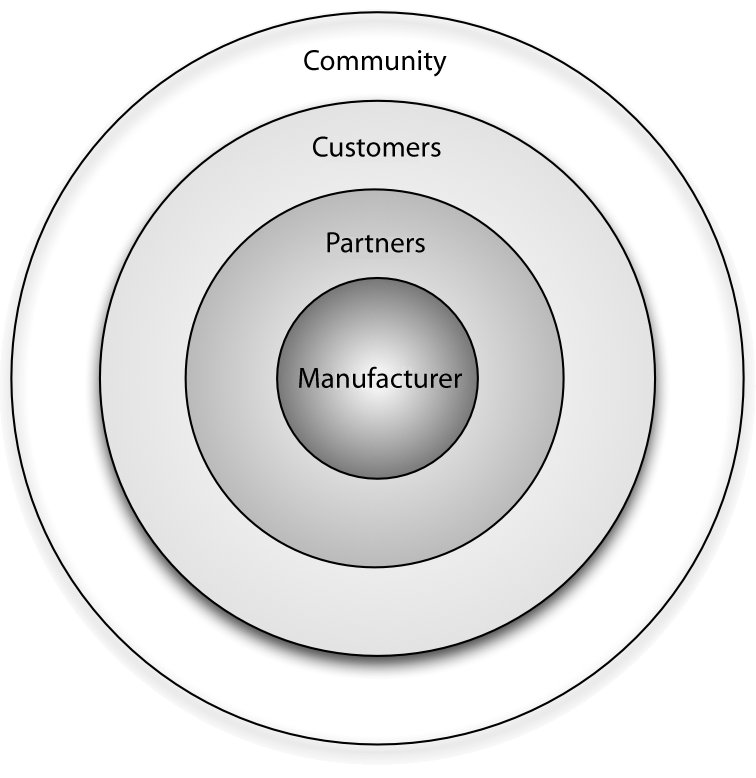
"Benefits of the community for partners of open source vendors"
Open source vendors can benefit from business ecosystems that form around their products. Partners of such vendors can utilize this ecosystem for their own business benefit by understanding the structure of the ecosystem, the key actors and their relationships, and the main levers of profitability. This article provides information on all of these aspects and identifies common business scenarios for partners of open source vendors. Armed with this information, partners can select a strategy that allows them to participate in the ecosystem while also maximizing their gains and driving adoption of their product or solution in the marketplace.
Every free/libre open source software (F/LOSS) vendor strives to create a business ecosystem around its software product. Doing this offers two primary advantages from a sales and marketing perspective: i) it increases the viability and longevity of the product in both commercial and communal spaces, and ii) it opens up new channels for communication and innovation. (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: January 11–17:
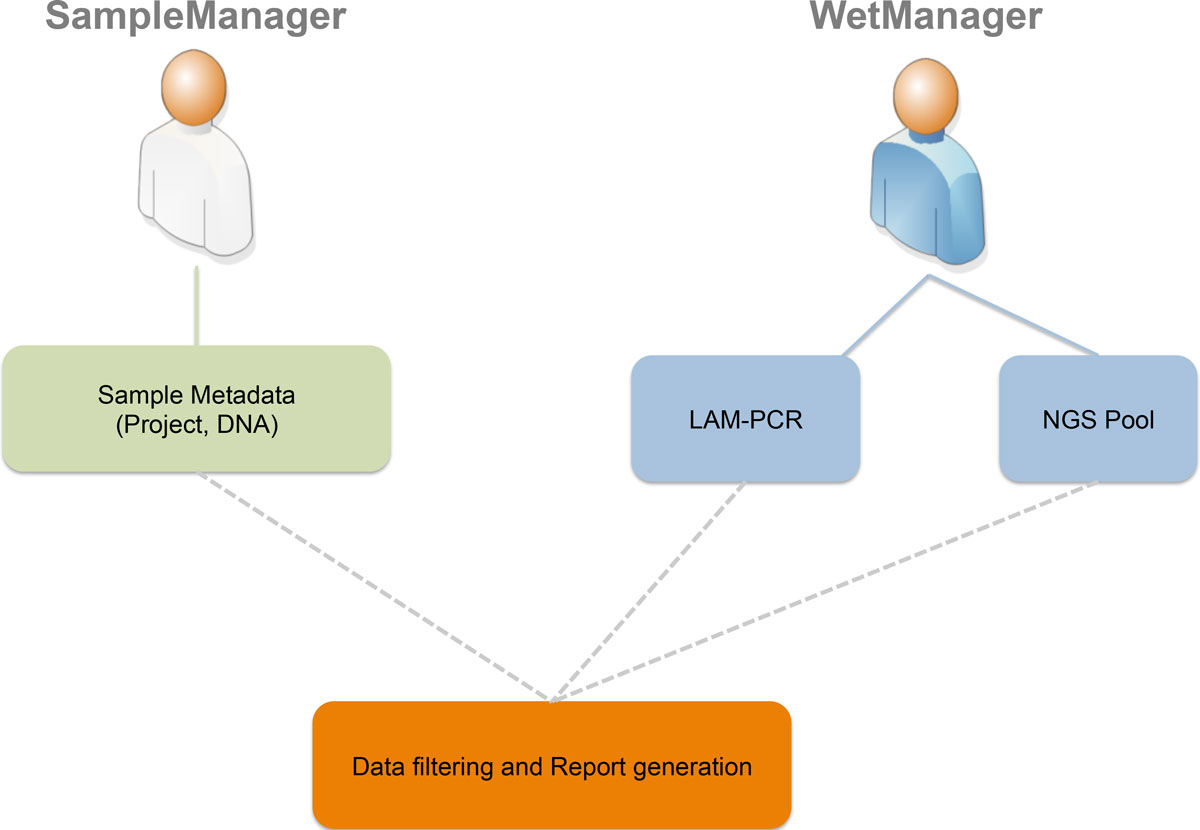
"adLIMS: A customized open source software that allows bridging clinical and basic molecular research studies"
Many biological laboratories that deal with genomic samples are facing the problem of sample tracking, both for pure laboratory management and for efficiency. Our laboratory exploits PCR techniques and Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) methods to perform high-throughput integration site monitoring in different clinical trials and scientific projects. Because of the huge amount of samples that we process every year, which result in hundreds of millions of sequencing reads, we need to standardize data management and tracking systems, building up a scalable and flexible structure with web-based interfaces, which are usually called Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS).
We extended and customized ADempiere ERP to fulfill LIMS requirements and we developed adLIMS. It has been validated by our end-users verifying functionalities and GUIs through test cases for PCRs samples and pre-sequencing data and it is currently in use in our laboratories. adLIMS implements authorization and authentication policies, allowing multiple users management and roles definition that enables specific permissions, operations and data views to each user. (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: January 4–10:
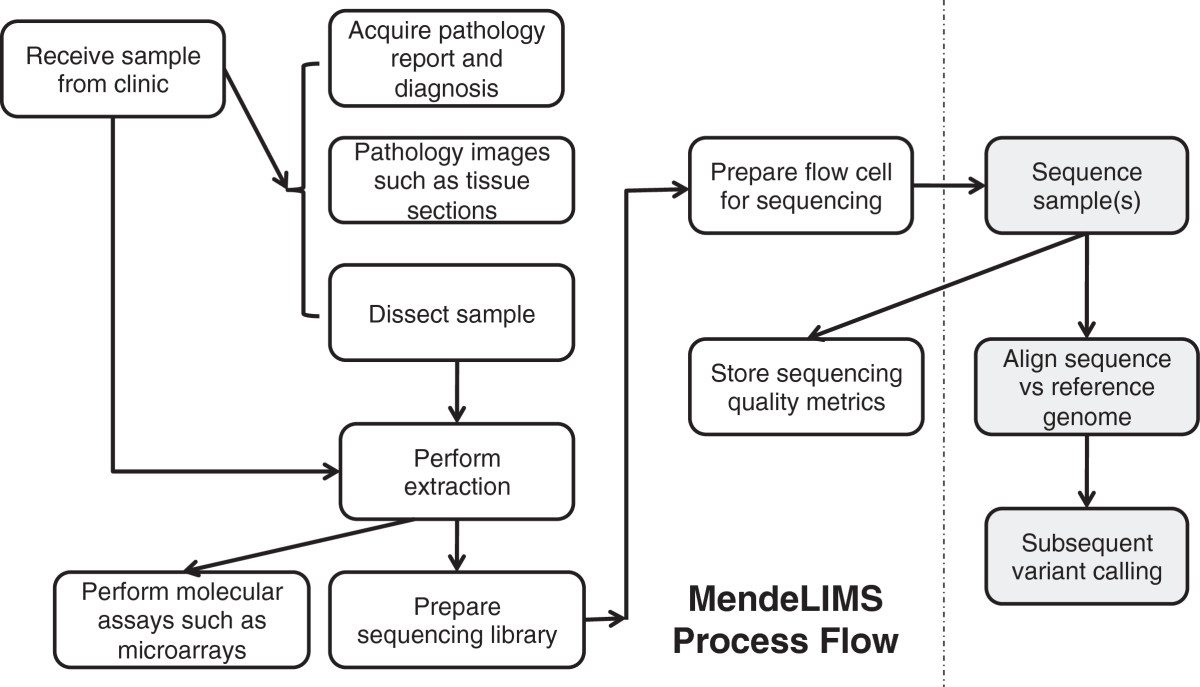
"MendeLIMS: A web-based laboratory information management system for clinical genome sequencing"
Large clinical genomics studies using next generation DNA sequencing require the ability to select and track samples from a large population of patients through many experimental steps. With the number of clinical genome sequencing studies increasing, it is critical to maintain adequate laboratory information management systems to manage the thousands of patient samples that are subject to this type of genetic analysis.
To meet the needs of clinical population studies using genome sequencing, we developed a web-based laboratory information management system (LIMS) with a flexible configuration that is adaptable to continuously evolving experimental protocols of next generation DNA sequencing technologies. Our system is referred to as MendeLIMS, is easily implemented with open source tools and is also highly configurable and extensible. MendeLIMS has been invaluable in the management of our clinical genome sequencing studies. (Full article...)
|
|