Journal:Analyzing huge pathology images with open source software
| Full article title | Analyzing huge pathology images with open source software |
|---|---|
| Journal | Diagnostic Pathology |
| Author(s) | Deroulers, Christophe; Ameisen, David; Badoual, Mathilde; Gerin, Chloé; Granier, Alexandre; Lartaud, Marc |
| Author affiliation(s) | Université Paris Diderot, Université Paris-Sud, Montpellier RIO Imaging, CIRAD |
| Primary contact | Email: deroulers@imnc.in2p3.fr |
| Year published | 2013 |
| Volume and issue | 8 |
| Page(s) | 92 |
| DOI | 10.1186/1746-1596-8-92 |
| ISSN | 1746-1596 |
| Distribution license | Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 Generic |
| Website | http://www.diagnosticpathology.org/content/8/1/92 |
| Download | http://www.diagnosticpathology.org/content/pdf/1746-1596-8-92.pdf (PDF) |
|
|
This article should not be considered complete until this message box has been removed. This is a work in progress. |
Abstract
Background
Digital pathology images are increasingly used both for diagnosis and research, because slide scanners are nowadays broadly available and because the quantitative study of these images yields new insights in systems biology. However, such virtual slides build up a technical challenge since the images occupy often several gigabytes and cannot be fully opened in a computer’s memory. Moreover, there is no standard format. Therefore, most common open source tools such as ImageJ fail at treating them, and the others require expensive hardware while still being prohibitively slow.
Results
We have developed several cross-platform open source software tools to overcome these limitations. The NDPITools provide a way to transform microscopy images initially in the loosely supported NDPI format into one or several standard TIFF files, and to create mosaics (division of huge images into small ones, with or without overlap) in various TIFF and JPEG formats. They can be driven through ImageJ plugins. The LargeTIFFTools achieve similar functionality for huge TIFF images which do not fit into RAM. We test the performance of these tools on several digital slides and compare them, when applicable, to standard software. A statistical study of the cells in a tissue sample from an oligodendroglioma was performed on an average laptop computer to demonstrate the efficiency of the tools.
Conclusions
Our open source software enables dealing with huge images with standard software on average computers. They are cross-platform, independent of proprietary libraries and very modular, allowing them to be used in other open source projects. They have excellent performance in terms of execution speed and RAM requirements. They open promising perspectives both to the clinician who wants to study a single slide and to the research team or data centre who do image analysis of many slides on a computer cluster.
Virtual slides
The virtual slide(s) for this article can be found here: http://www.diagnosticpathology.diagnomx.eu/vs/5955513929846272
Keywords: Digital pathology; Image processing; Virtual slides; Systems biology; ImageJ; NDPI
Background
Virtual microscopy has become routinely used over the last few years for the transmission of pathology images (the so-called virtual slides), for both telepathology and teaching.[1][2] In more and more hospitals, virtual slides are even attached to the patient’s file.[3][4] They have also a great potential for research, especially in the context of multidisciplinary projects involving e.g. mathematicians and clinicians who do not work at the same location. Quantitative histology is a promising new field, involving computer-based morphometry or statistical analysis of tissues.[5][6][7][8][9] A growing number of works report the pertinence of such images for diagnosis and classification of diseases, e.g. tumours.[10][11][12][13][14] Databases of clinical cases[15] will include more and more digitized tissue images. This growing use of virtual microscopy is accompanied by the development of integrated image analysis systems offering both virtual slide scanning and automatic image analysis, which makes integration into the daily practice of pathologists easier. See Ref. 16[16] for a review of some of these systems.
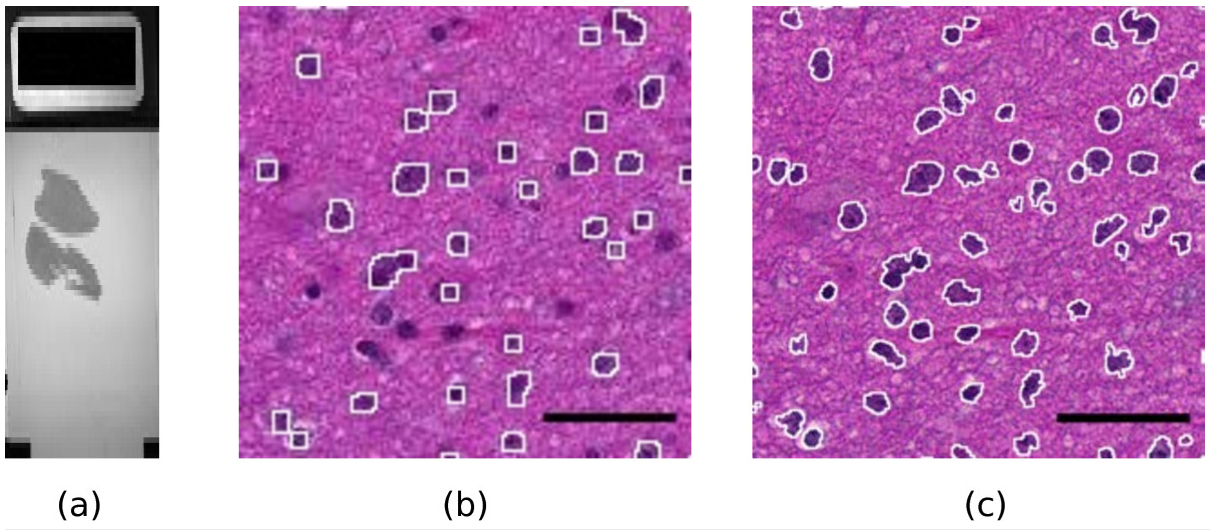
Modern slide scanners produce high magnification microscopy images of excellent quality[1], for instance at the so-called “40x” magnification. They allow much better visualization and analysis than lower magnification images. As an example, Figure 1 shows two portions of a slide at different magnifications, 10x and 40x. The benefit of the high magnification for both diagnosis and automated image analysis is clear. For instance, the state of the chromatin inside the nucleus and the cell morphology, better seen at high magnification, are essential to help the clinician distinguish tumorous and non-tumorous cells. An accurate, non-pixelated determination of the perimeters of the cell nuclei is needed for morphometry and statistics.
Figure 1. A sample slide. (a): macroscopic view of the whole slide (the black rectangle on the left is 1x2 cm).
(b,c): Influence of the magnification on the quality of results. (b): a portion of the slide scanned at magnification
level 10x. The white contours show the result of an automatic detection of the dark cell nuclei with the ImageJ
software. A significant fraction of the cell nuclei is missed and the contours are rather pixelated. (c): the same
portion of the slide scanned at magnification 40x. The white contours show the result of the same automatic
detection. Almost all cell nuclei are detected and the shapes of the contours are much more precise.
Scale bar: 4 μm.
However, this technique involves the manipulation of huge images (of the order of 10 billions of pixels for a full-size slide at magnification 40x with a single focus level) for which the approach taken by most standard software, loading and decompressing the full image into RAM, is impossible (a single slice of a full-size slide needs of the order of 30 GiB of RAM). As a result, standard open-source software such as ImageJ[17], ImageMagick[18] or GraphicsMagick[19] completely fails or is prohibitively slow when used on these images. Of course, commercially available software exists[16], but it is usually quite expensive, and very often restricted to a single operating system. It uses proprietary source code, which is a problem if one wants to control or check the algorithms and their parameters when doing image analysis for research.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Diamond, J.; McCleary, D. (2009). "Virtual Microscopy". In Hannon-Fletcher, M.; Maxwell, P.. Advanced Techniques in Diagnostic Cellular Pathology. Chichester UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. ISBN 9780470515976.
- ↑ Ameisen, D.; Yunès, J.B.; Deroulers, C.; Perrier, V.; Bouhidel, F.; Battistella, M.; Legrès, L.; Janin, A.; Bertheau, P. (2013). "Stack or Trash? Fast quality assessment of virtual slides". Diagnostic Pathology 8 (Suppl 1): S23. doi:10.1186/1746-1596-8-S1-S23. PMC PMC3849546. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3849546.
- ↑ García Rojo, M.; Castro, A.M.; Gonçalves, L. (2011). "COST action “EuroTelepath”: digital pathology integration in electronic health record, including primary care centres". Diagnostic Pathology 6 (Suppl 1): S6. doi:10.1186/1746-1596-6-S1-S6. PMC PMC3073224. PMID 21489201. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3073224.
- ↑ Ameisen, D. (2013). "Intégration des lames virtuelles dans le dossier patient électronique". PhD thesis. Univ Paris Diderot-Paris 7.
- ↑ Collan, Y.; Torkkeli, T.; Personen, E.; Jantunen, E.; Kosma, V.M. (1987). "Application of morphometry in tumor pathology". Analytical and Quantitative Cytology and Histology 9 (2): 79–88. PMID 3300687.
- ↑ Wolfe, P.; Murphy, J.; McGinley, J.; Zhu, Z.; Jiang, W.; Gottschall, E.; Thompson, H. (2004). "Using nuclear morphometry to discriminate the tumorigenic potential of cells: A comparison of statistical methods". Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention 13 (6): 976–988. PMID 15184254.
- ↑ Gürcan, M.N.; Boucheron, L.E.; Can, A.; Madabhushi, A.; Rajpoot, N.M.; Yener, B. (2009). "Histopathological image analysis: a review". IEEE Reviews in Biomedical Engineering 2009 (2): 147–171. doi:10.1109/RBME.2009.2034865. PMC PMC2910932. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2910932.
- ↑ Gerin, C.; Pallud, J.; Deroulers, C.; Varlet, P.; Oppenheim, C.; Roux, F.X.; Chrétien, F.; Thomas, S.R.; Grammaticos, B.; Badoual, M. (2013). "Quantitative characterization of the imaging limits of diffuse low-grade oligodendrogliomas". Neuro-Oncology 15 (10): 1379-88. doi:10.1093/neuonc/not072. PMC PMC3779035. PMID 23771168. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3779035.
- ↑ Wienert, S.; Heim, D.; Kotani, M.; Lindequist, B.; Stenzinger, A.; Ishii, M.; Hufnagl, P.; Beil, M.; Dietel, M.; Denkert, C.; Klauschen, F. (2013). "CognitionMaster: an object-based image analysis framework". Diagnostic Pathology 8: 34. doi:10.1186/1746-1596-8-34. PMC PMC3626931. PMID 23445542. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3626931.
- ↑ Gunduz, C.; Yener, B.; Gultekin, S.H. (2004). "The cell graphs of cancer". Bioinformatics 20 (Suppl 1): i145-i151. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bth933. PMID 15262793.
- ↑ Gunduz, C.; Gultekin, S.H.; Yener, B. (2005). "Augmented cell-graphs for automated cancer diagnosis". Bioinformatics 21 (Suppl 2): ii7-ii12. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bti1100. PMID 16204128.
- ↑ West, N.P.; Dattani, M.; McShane, P.; Hutchins, G.; Grabsch, J.; Mueller, W.; Treanor, D.; Quirke, P.; Grabsch, H. (2010). "The proportion of tumour cells is an independent predictor for survival in colorectal cancer patients". British Journal of Cancer 102 (10): 1519–1523. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605674. PMC PMC2869173. PMID 20407439. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2869173.
- ↑ Chang, H.; Han, J.; Borowsky, A.; Loss, L.; Gray, J.W.; Spellman, P.T.; Parvin, B. (2013). "Invariant delineation of nuclear architecture in Glioblastoma multiforme for clinical and molecular association". IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 32 (4): 670–682. doi:10.1109/TMI.2012.2231420. PMC PMC3728287. PMID 23221815. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3728287.
- ↑ Kayser, K.; Radziszowski, D.; Bzdyl, P.; Sommer, R.; Kayser, G. (2006). "Towards an automated virtual slide screening: theoretical considerations and practical experiences of automated tissue-based virtual diagnosis to be implemented in the internet". Diagnostic Pathology 1: 10. doi:10.1186/1746-1596-1-10. PMC PMC1524814. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1524814.
- ↑ PLGA Foundation (2012). "Meta analysis low grade glioma database project". Archived from the original on 11 July 2013. http://www.webcitation.org/query.php?url=http://www.fightplga.org/research/PLGA-Sponsored_Projects/MetaAnalysis&refdoi=10.1186/1746-1596-8-92.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 García Rojo, M.; Bueno, G.; Slodkowska, J. (2009). "Review of imaging solutions for integrated quantitative immunohistochemistry in the Pathology daily practice". Folia Histochemica et Cytobiologica 47 (3): 349–354. doi:10.2478/v10042-008-0114-4. PMID 20164017.
- ↑ Rasband, W.S. (2012). "ImageJ". http://imagej.nih.gov/ij/.
- ↑ ImageMagick Studio, LLC (2013). "ImageMagick". http://www.imagemagick.org/.
- ↑ GraphicsMagick Group (2013). "GraphicsMagick". http://www.graphicsmagick.org/.
Notes
This presentation is faithful to the original, with only a few minor changes to presentation. In most of the article's references DOIs and PubMed IDs were not given; they've been added to make the references more useful. In some cases important information was missing from the references, and that information was added.