Featured article of the week: February 28–March 05:"Designing a knowledge management system for naval materials failures"
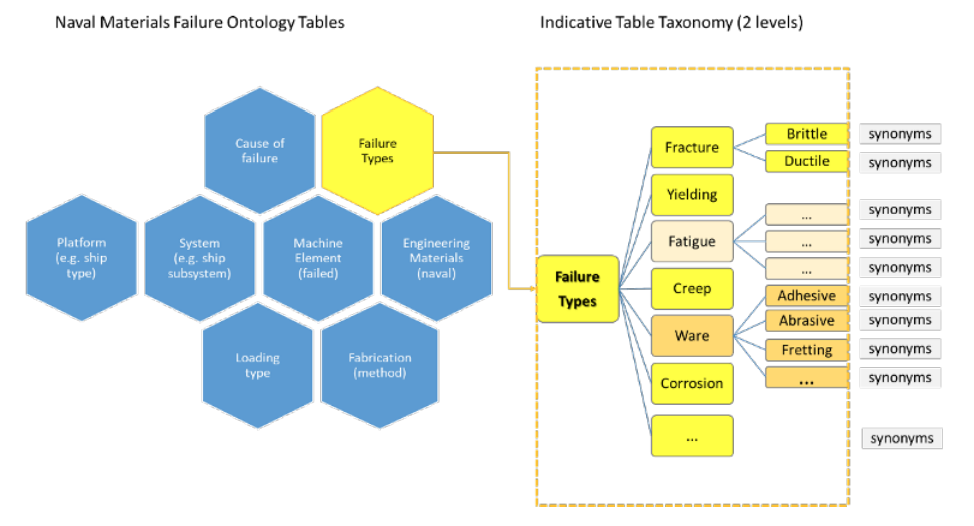
Implemented materials fail from time to time, requiring failure analysis. This type of scientific analysis expands into forensic engineering for it aims not only to identify individual and symptomatic reasons for failure, but also to assess and understand repetitive failure patterns, which could be related to underlying material faults, design mistakes, or maintenance omissions. Significant information can be gained and studied from carefully documenting and managing the data that comes from failure analysis of materials, including in the naval industry. The NAVMAT research project, presented herein, attempts an interdisciplinary approach to materials informatics by integrating materials engineering and informatics under a platform of knowledge management. Our approach utilizes a focused, common-cause failure analysis methodology for the naval and marine environment. The platform's design is dedicated to the effective recording, efficient indexing, and easy and accurate retrieval of relevant information, including the associated history of maintenance and secure operation concerning failure incidents of marine materials, components, and systems in an organizational fleet. ... (Full article...)
Featured article of the week: February 20–27:
"Laboratory information management system for COVID-19 non-clinical efficacy trial data"
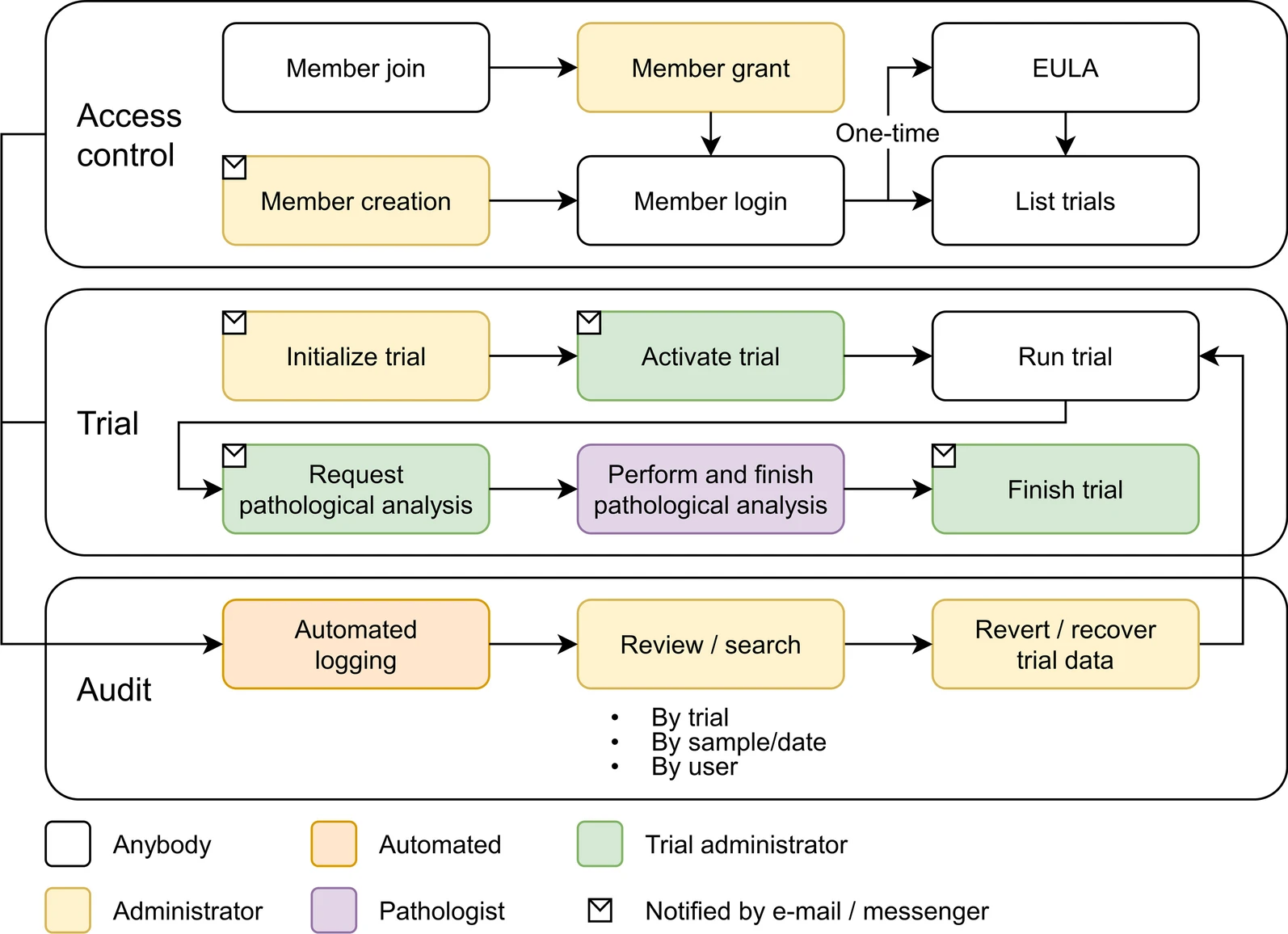
As the number of large-scale research studies involving multiple organizations producing data has steadily increased, an integrated system for a common interoperable data format is needed. For example, in response to the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, a number of global efforts are underway to develop vaccines and therapeutics. We are therefore observing an explosion in the proliferation of COVID-19 data, and interoperability is highly requested in multiple institutions participating simultaneously in COVID-19 pandemic research. In this study, a laboratory information management system (LIMS) has been adopted to systemically manage, via web interface, various COVID-19 non-clinical trial data—including mortality, clinical signs, body weight, body temperature, organ weights, viral titer (viral replication and viral RNA), and multi-organ histopathology—from multiple institutions ... (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: February 13–19:
"Improving data quality in clinical research informatics tools"
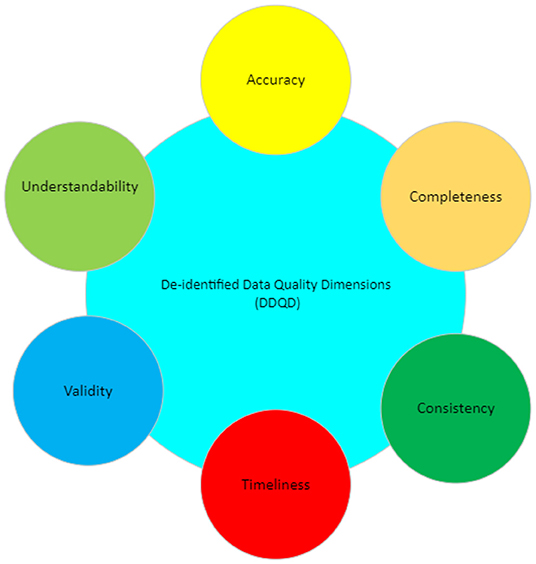
Maintaining data quality is a fundamental requirement for any successful and long-term data management project. Providing high-quality, reliable, and statistically sound data is a primary goal for clinical research informatics. In addition, effective data governance and management are essential to ensuring accurate data counts, reports, and validation. As a crucial step of the clinical research process, it is important to establish and maintain organization-wide standards for data quality management to ensure consistency across all systems designed primarily for cohort identification ... (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: February 6–12:
"Electronic tools in clinical laboratory diagnostics: Key examples, limitations, and value in laboratory medicine"
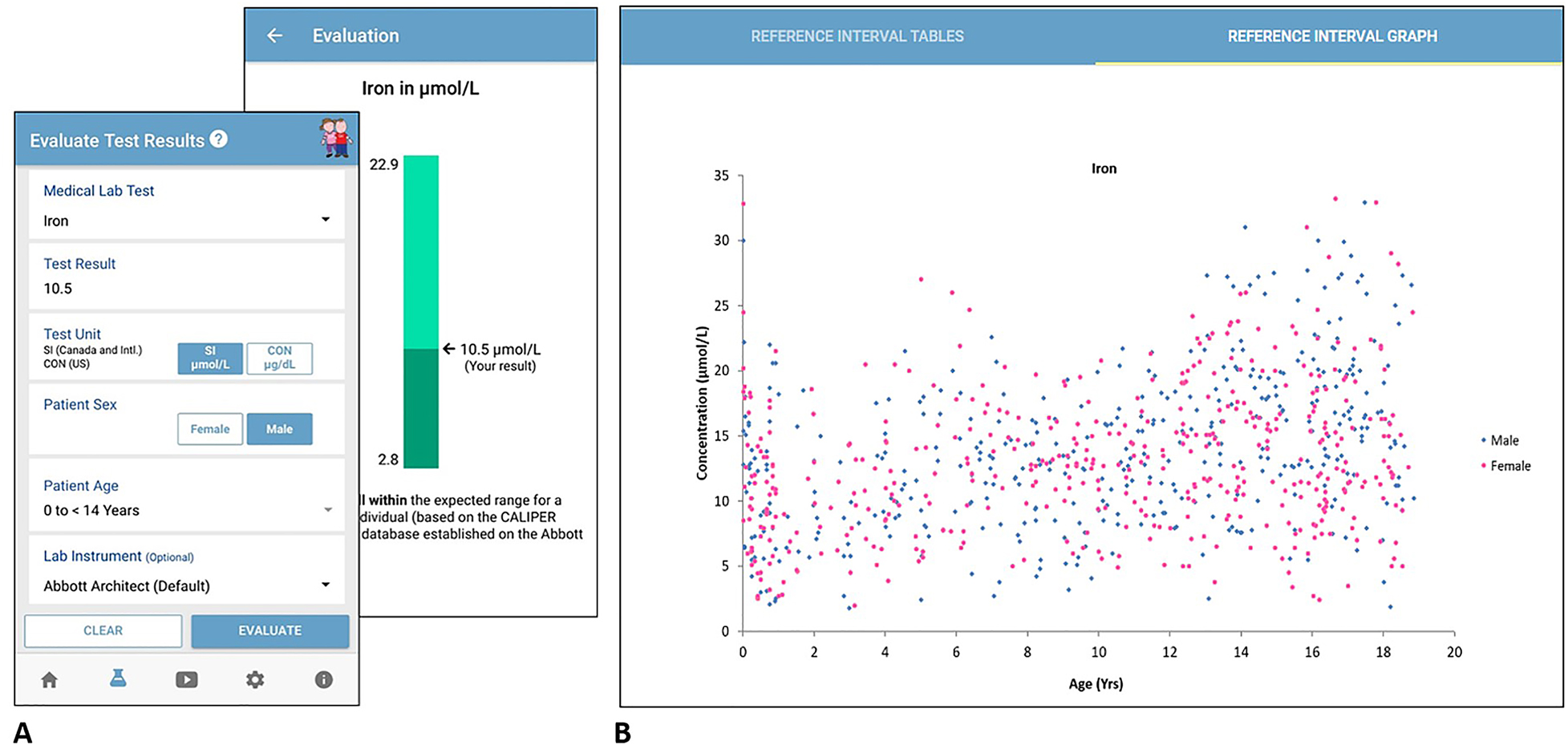
Electronic tools in clinical laboratory diagnostics can assist laboratory professionals, clinicians, and patients in medical diagnostic management and laboratory test interpretation. With increasing implementation of electronic health records (EHRs) and laboratory information systems (LIS) worldwide, there is increasing demand for well-designed and evidence-based electronic resources. Both complex data-driven and simple interpretative electronic healthcare tools are currently available to improve the integration of clinical and laboratory information towards a more patient-centered approach to medicine. Several studies have reported positive clinical impact of electronic healthcare tool implementation in clinical laboratory diagnostics, including in the management of neonatal bilirubinemia, cardiac disease, and nutritional status ... (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: January 30–February 5:
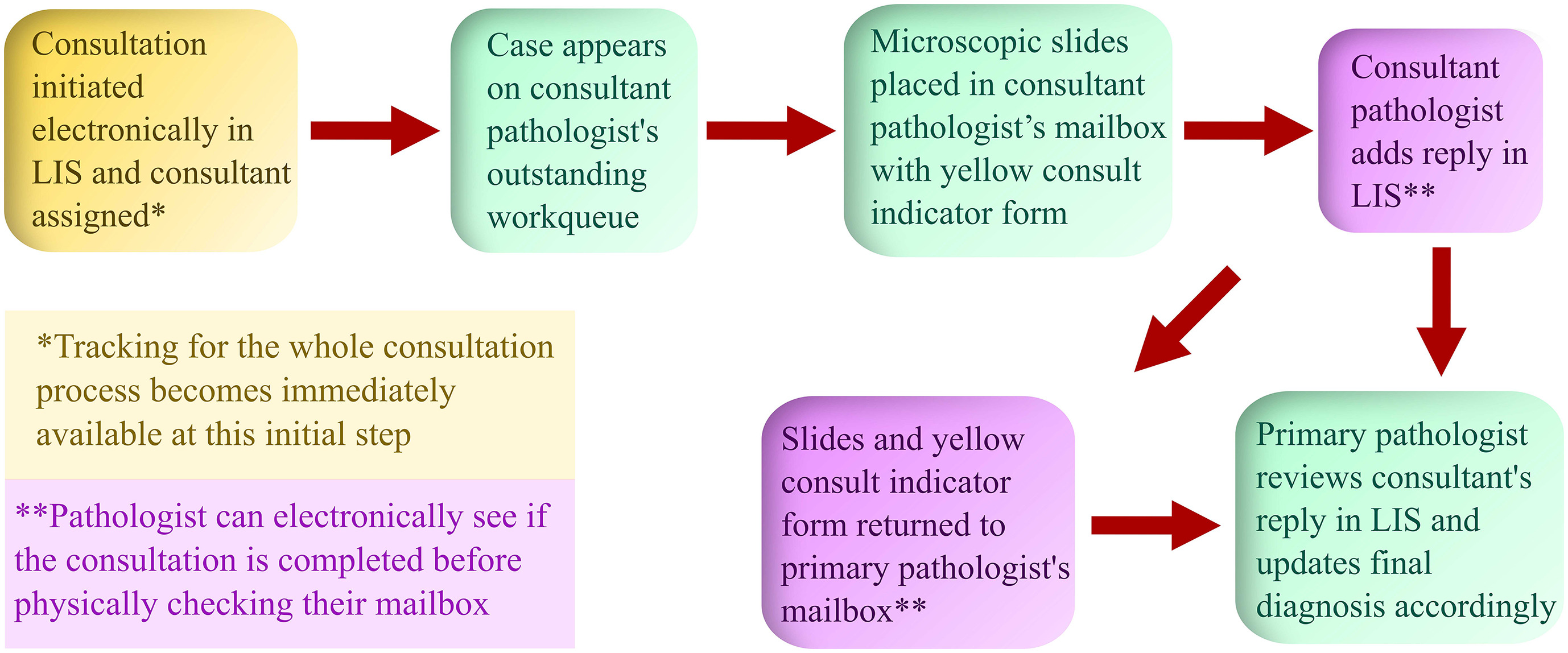
"Anatomic pathology quality assurance: Developing an LIS-based tracking and documentation module for intradepartmental consultations"
An electronic intradepartmental consultation system for anatomic pathology (AP) was conceived and developed in the laboratory information system (LIS) of University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics in 2019. Previously, all surgical pathology intradepartmental consultative activities were initiated and documented with paper forms, which were circulated with the pertinent microscopic slides and were eventually filed. In this study, we discuss the implementation and utilization of an electronic intradepartmental AP consultation system. Workflows and procedures were developed to organize intradepartmental surgical pathology consultations from the beginning to the end point of the consultative activities entirely using a paperless system that resided in the LIS ... (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: January 23–29:
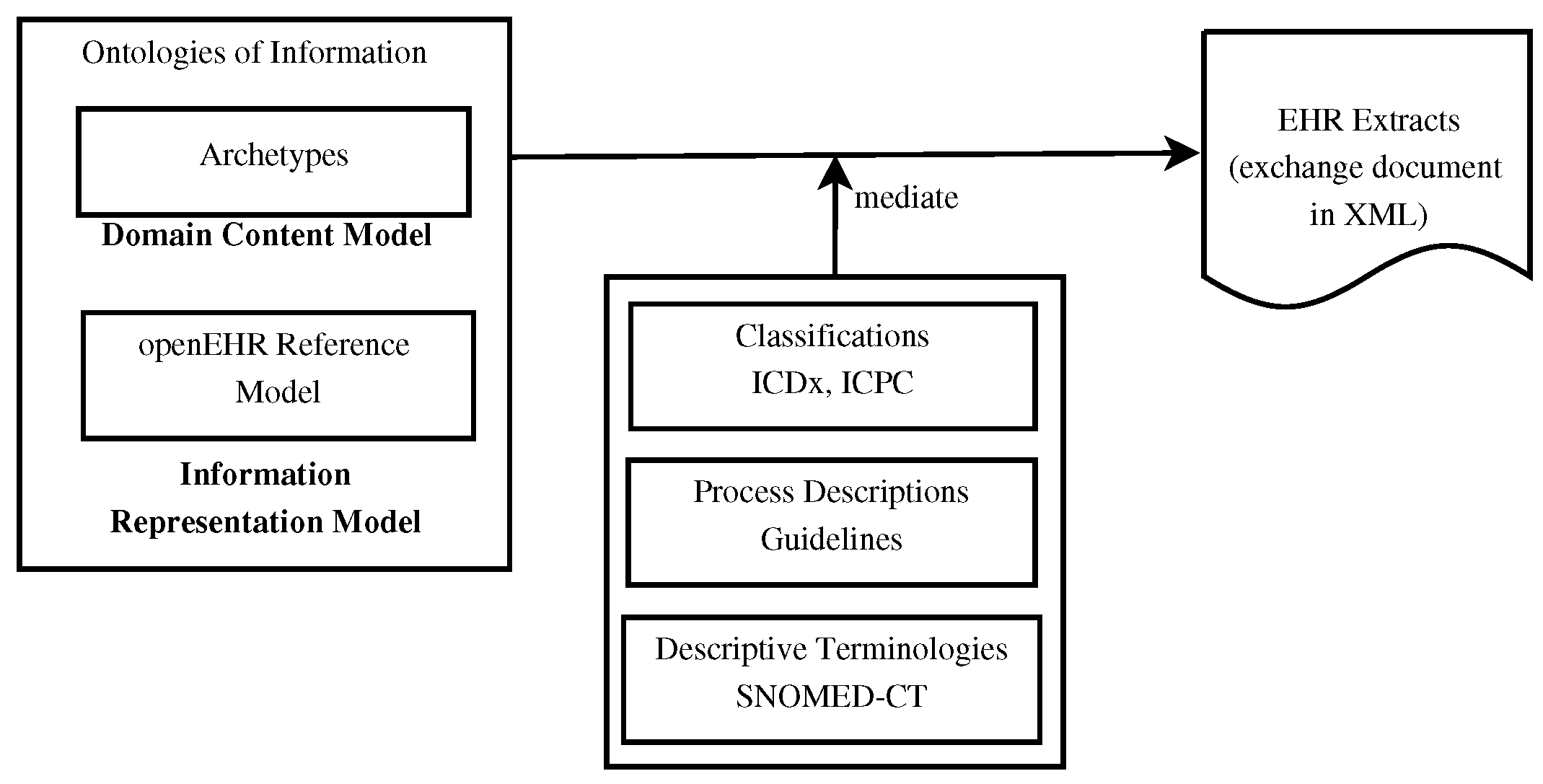
"Using knowledge graph structures for semantic interoperability in electronic health records data exchanges"
Information sharing across medical institutions is restricted to information exchange between specific partners. The lifelong electronic health record (EHR) structure and content require standardization efforts. Existing standards such as openEHR, Health Level 7 (HL7), and ISO/EN 13606 aim to achieve data independence along with semantic interoperability. This study aims to discover knowledge representation to achieve semantic health data exchange. openEHR and ISO/EN 13606 use archetype-based technology for semantic interoperability. The HL7 Clinical Document Architecture is on its way to adopting this through HL7 templates. Archetypes are the basis for knowledge-based systems, as these are means to define clinical knowledge. The paper examines a set of formalisms for the suitability of describing, representing, and reasoning about archetypes ... (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: January 16–22:
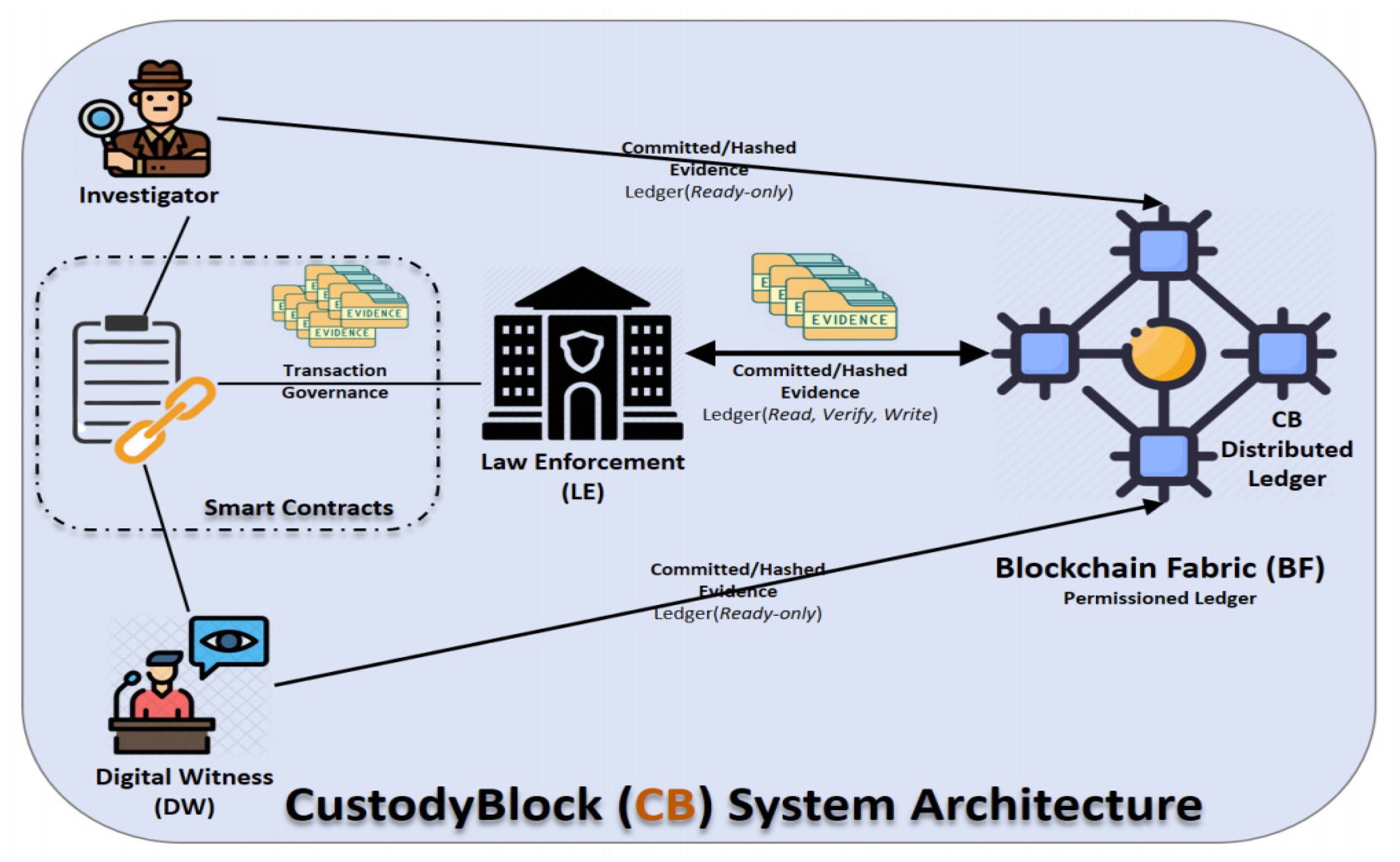
"CustodyBlock: A distributed chain of custody evidence framework"
With the increasing number of cybercrimes, the digital forensics team has no choice but to implement more robust and resilient evidence-handling mechanisms. The capturing of digital evidence, which is a tangible and probative piece of information that can be presented in court and used in trial, is challenging due to its volatility and the possible effects of improper handling procedures. When computer systems get compromised, digital forensics comes into play to analyze, discover, extract, and preserve all relevant evidence. Therefore, it is imperative to maintain efficient evidence management to guarantee the credibility and admissibility of digital evidence in a court of law. A critical component of this process is to utilize an adequate chain of custody (CoC) approach to preserve the evidence in its original state from compromise and/or contamination ... (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: January 09–15:
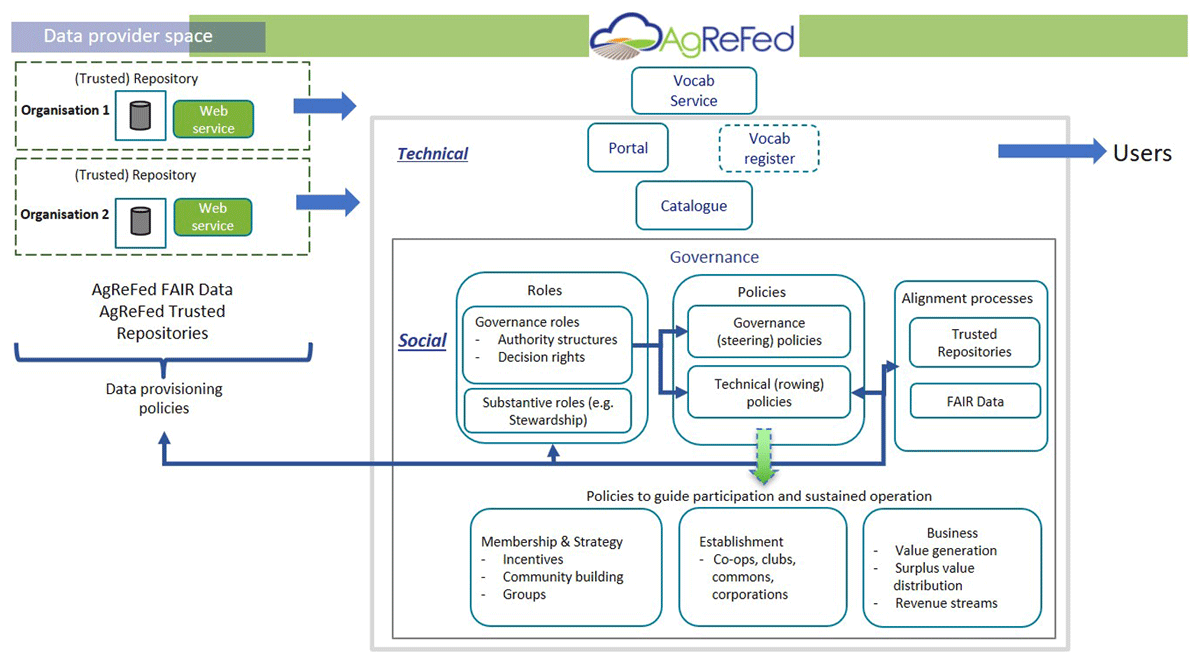
"Development and governance of FAIR thresholds for a data federation"
The FAIR (findable, accessible, interoperable, and re-usable) principles and practice recommendations provide high-level guidance and recommendations that are not research-domain specific in nature. There remains a gap in practice at the data provider and domain scientist level, demonstrating how the FAIR principles can be applied beyond a set of generalist guidelines to meet the needs of a specific domain community. We present our insights developing FAIR thresholds in a domain-specific context for self-governance by a community (in this case, agricultural research). "Minimum thresholds" for FAIR data are required to align expectations for data delivered from providers’ distributed data stores through a community-governed federation (the Agricultural Research Federation, AgReFed) ... (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: January 02–08:
"Design of a data management reference architecture for sustainable agriculture"
Effective and efficient data management is crucial for smart farming and precision agriculture. To realize operational efficiency, full automation, and high productivity in agricultural systems, different kinds of data are collected from operational systems using different sensors, stored in different systems, and processed using advanced techniques, such as machine learning and deep learning. Due to the complexity of data management operations, a data management reference architecture is required. While there are different initiatives to design data management reference architectures, a data management reference architecture for sustainable agriculture is missing. In this study, we follow domain scoping, domain modeling, and reference architecture design stages to design the reference architecture for sustainable agriculture. Four case studies were performed to demonstrate the applicability of the reference architecture. This study shows that the proposed data management reference architecture is practical and effective for sustainable agriculture ... (Full article...)
|
|