Difference between revisions of "Main Page/Featured article of the week/2024"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Added last week's article of the week) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Added last week's article of the week) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
<!-- Below this line begin pasting previous news --> | <!-- Below this line begin pasting previous news --> | ||
<h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: February 19–25:</h2> | <h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: February 26–March 03:</h2> | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Pineda-Pampliega EFSAJournal2023 20-S2.png|240px]]</div> | |||
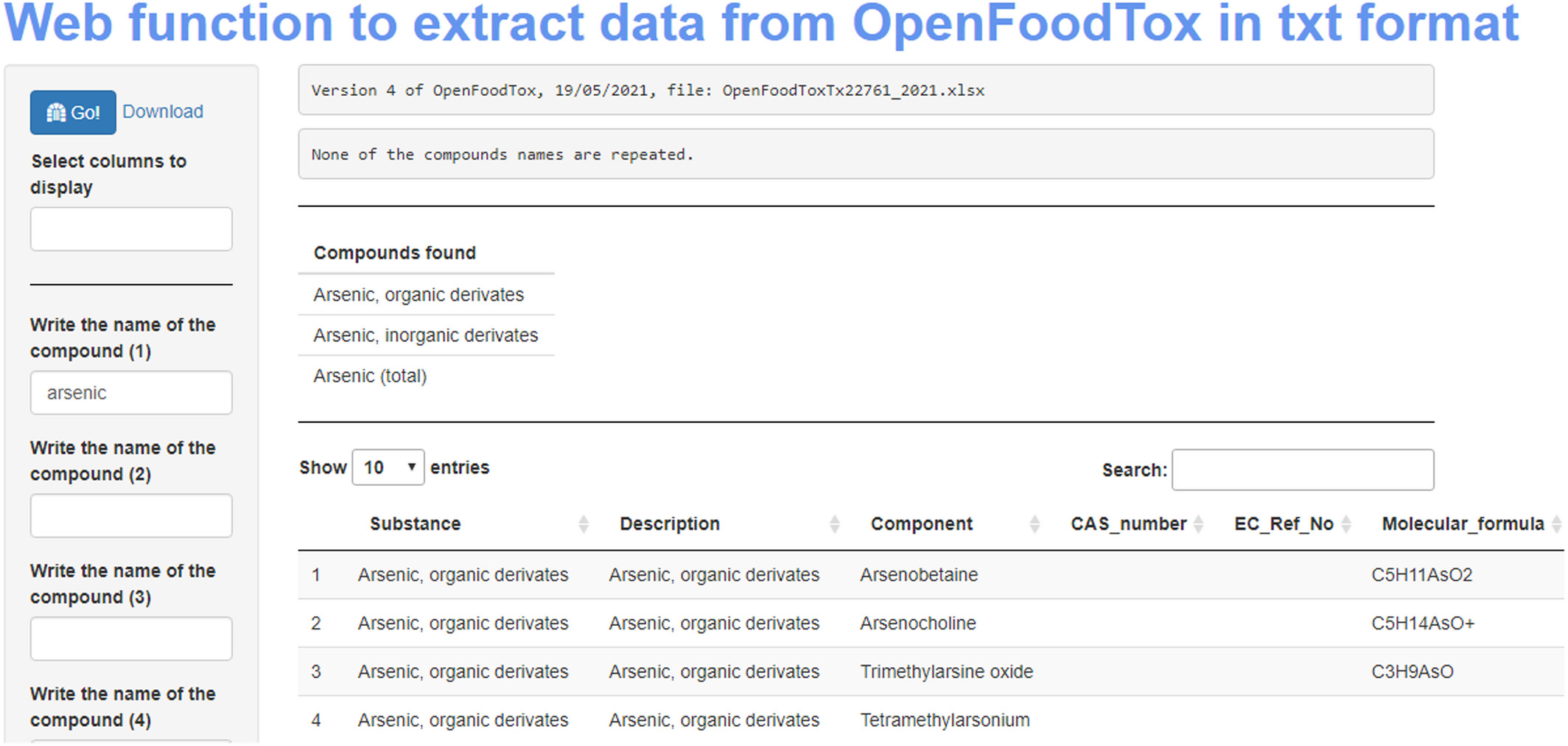
'''"[[Journal:Developing a framework for open and FAIR data management practices for next generation risk- and benefit assessment of fish and seafood|Developing a framework for open and FAIR data management practices for next generation risk- and benefit assessment of fish and seafood]]"''' | |||
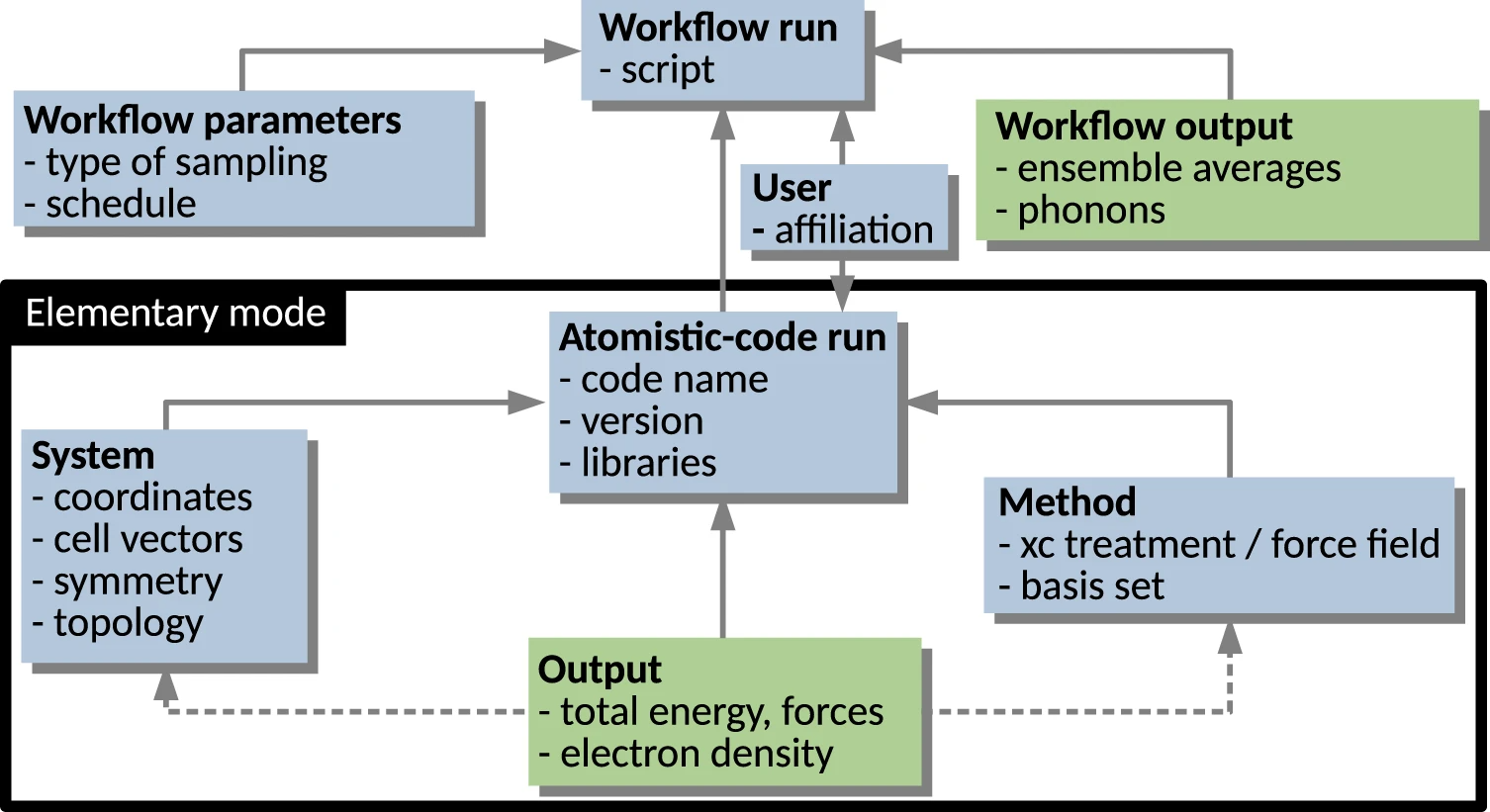
[[Risk assessment|Risk and risk–benefit assessments]] of food are complex exercises, in which access to and use of several disconnected individual stand-alone [[database]]s is required to obtain hazard and exposure information. Data obtained from such databases ideally should be in line with the [[Journal:The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship|FAIR principles]], i.e. the data must be findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable. However, often cases are encountered when one or more of these principles are not followed. In this project, we set out to assess if existing commonly used databases in risk assessment are in line with the FAIR principles ... ('''[[Journal:Developing a framework for open and FAIR data management practices for next generation risk- and benefit assessment of fish and seafood|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: February 19–25:</h2> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig2 Henke JMIRMedInfo2023 11.png|240px]]</div> | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig2 Henke JMIRMedInfo2023 11.png|240px]]</div> | ||
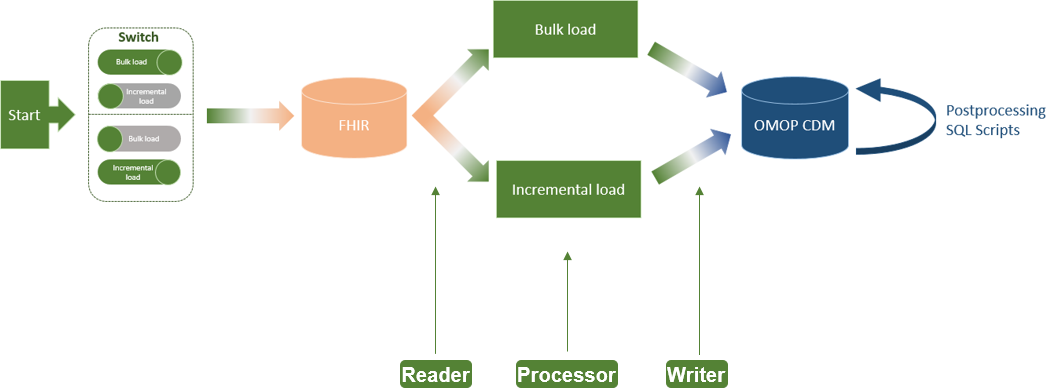
'''"[[Journal:An extract-transform-load process design for the incremental loading of German real-world data based on FHIR and OMOP CDM: Algorithm development and validation|An extract-transform-load process design for the incremental loading of German real-world data based on FHIR and OMOP CDM: Algorithm development and validation]]"''' | '''"[[Journal:An extract-transform-load process design for the incremental loading of German real-world data based on FHIR and OMOP CDM: Algorithm development and validation|An extract-transform-load process design for the incremental loading of German real-world data based on FHIR and OMOP CDM: Algorithm development and validation]]"''' | ||
Revision as of 15:21, 4 March 2024
|
|
If you're looking for other "Article of the Week" archives: 2014 - 2015 - 2016 - 2017 - 2018 - 2019 - 2020 - 2021 - 2022 - 2023 - 2024 |
Featured article of the week archive - 2024
Welcome to the LIMSwiki 2024 archive for the Featured Article of the Week.
Featured article of the week: February 26–March 03:Risk and risk–benefit assessments of food are complex exercises, in which access to and use of several disconnected individual stand-alone databases is required to obtain hazard and exposure information. Data obtained from such databases ideally should be in line with the FAIR principles, i.e. the data must be findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable. However, often cases are encountered when one or more of these principles are not followed. In this project, we set out to assess if existing commonly used databases in risk assessment are in line with the FAIR principles ... (Full article...)
|