Difference between revisions of "Journal:VennDiagramWeb: A web application for the generation of highly customizable Venn and Euler diagrams"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Created stub. Saving and adding more.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Saving and adding more.) |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
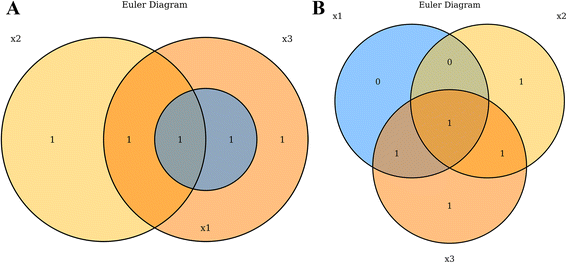
Venn and Euler diagrams are used frequently in computational biology to visualize the interactions between multiple sets of data. In [[genomics]] especially, a common assay is to compare gene lists occurring from separate analyses<ref name="Bardou_jvenn14">{{cite journal |title=jvenn: An interactive Venn diagram viewer |journal=BMC Bioinformatics |author=Bardou, P.; Mariette, J.; Escudié, F. et al. |volume=15 |pages=293 |year=2014 |doi=10.1186/1471-2105-15-293 |pmid=25176396 |pmc=PMC4261873}}</ref>, such as contrasting lists of differentially abundant RNAs following drug treatments or lists of mutated genes across disease types. Venn diagrams are typically depicted as partially intersecting circles or other closed curves such that there are 2<sup>n</sup> separated regions as depicted by overlapping closed curves.<ref name="WeissteinVenn">{{cite web |url=http://mathworld.wolfram.com/VennDiagram.html |title=Venn Diagram |work=MathWorld |publisher=Wolfram Research, Inc |accessdate=22 August 2016}}</ref> While Venn diagrams always depict all 2<sup>n</sup> possible regions, Euler diagrams can omit regions under which there are zero values in that region’s subset. This allows Euler diagrams to be less visually complex, by depicting only a subset of all possible regions.<ref name="RodgerEuler04">{{cite web |url=https://www.cs.kent.ac.uk/events/conf/2004/euler/eulerdiagrams.html |title=Venn Diagrams, Euler Diagrams and Leibniz |work=Euler Diagrams 2004 |author=Rodger, P. |date=22 September 2004 |accessdate=22 August 2016}}</ref> ''VennDiagramWeb'' facilitates the creation of both Venn and Euler diagrams, using the argument euler.d and scaled (both default TRUE). By default, ''VennDiagramWeb'' will create an Euler diagram where possible, displaying only regions containing one or more values. Users can force Venn diagrams only by setting both euler.d = FALSE and scaled = FALSE (Fig. 1). | Venn and Euler diagrams are used frequently in computational biology to visualize the interactions between multiple sets of data. In [[genomics]] especially, a common assay is to compare gene lists occurring from separate analyses<ref name="Bardou_jvenn14">{{cite journal |title=jvenn: An interactive Venn diagram viewer |journal=BMC Bioinformatics |author=Bardou, P.; Mariette, J.; Escudié, F. et al. |volume=15 |pages=293 |year=2014 |doi=10.1186/1471-2105-15-293 |pmid=25176396 |pmc=PMC4261873}}</ref>, such as contrasting lists of differentially abundant RNAs following drug treatments or lists of mutated genes across disease types. Venn diagrams are typically depicted as partially intersecting circles or other closed curves such that there are 2<sup>n</sup> separated regions as depicted by overlapping closed curves.<ref name="WeissteinVenn">{{cite web |url=http://mathworld.wolfram.com/VennDiagram.html |title=Venn Diagram |work=MathWorld |publisher=Wolfram Research, Inc |accessdate=22 August 2016}}</ref> While Venn diagrams always depict all 2<sup>n</sup> possible regions, Euler diagrams can omit regions under which there are zero values in that region’s subset. This allows Euler diagrams to be less visually complex, by depicting only a subset of all possible regions.<ref name="RodgerEuler04">{{cite web |url=https://www.cs.kent.ac.uk/events/conf/2004/euler/eulerdiagrams.html |title=Venn Diagrams, Euler Diagrams and Leibniz |work=Euler Diagrams 2004 |author=Rodger, P. |date=22 September 2004 |accessdate=22 August 2016}}</ref> ''VennDiagramWeb'' facilitates the creation of both Venn and Euler diagrams, using the argument euler.d and scaled (both default TRUE). By default, ''VennDiagramWeb'' will create an Euler diagram where possible, displaying only regions containing one or more values. Users can force Venn diagrams only by setting both euler.d = FALSE and scaled = FALSE (Fig. 1). | ||
[[File:Fig1 Lam BMCBioinformatics2016 17.gif|567px]] | |||
{{clear}} | |||
{| | |||
| STYLE="vertical-align:top;"| | |||
{| border="0" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" width="567px" | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"| <blockquote>'''Figure 1.''' '''Figure 1.''' Euler and Venn diagrams produced by ''VennDiagramWeb'' each depicting three sets: x1 = {7,8}, x2 = {4,6,7}, x3 = {4,7,8,10}. '''a'''. An Euler diagram, produced with euler.d = TRUE and scaled = TRUE. '''b'''. A Venn diagram, produced with euler.d = FALSE and scaled = FALSE.</blockquote> | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
|} | |||
The R statistical programming language has widespread use in the bioinformatics field, and so we developed VennDiagram to generate plots in this language.<ref name="ChenVenn11">{{cite journal |title=VennDiagram: A package for the generation of highly-customizable Venn and Euler diagrams in R |journal=BMC Bioinformatics |author=Chen, H.; Boutros, P.C. |volume=12 |pages=35 |year=2011 |doi=10.1186/1471-2105-12-35 |pmid=21269502 |pmc=PMC3041657}}</ref> The initial release has proven to be robust and useful, and has garnered 186 citations. As of June 8, 2016 the package has been downloaded from the Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN) over 75,000 times since its release in March 2011. Over half of these (>40,000) occurred in 2015 alone, highlighting growing popularity.<ref name="Csárdi_cranlogs">{{cite web |url=https://github.com/metacran/cranlogs |title=cranlogs: Download Logs from the RStudio CRAN Mirror |work=GitHub |publisher=GitHub, Inc |accessdate=08 June 2016}}</ref> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 22:32, 11 October 2016
| Full article title | VennDiagramWeb: A web application for the generation of highly customizable Venn and Euler diagrams |
|---|---|
| Journal | BMC Bioinformatics |
| Author(s) | Lam, F.; Lalansingh, C.M.; Babaran, H.E.; Wang, Z.; Prokepec, S.D.; Fox, N.S.; Boutros, P.C. |
| Author affiliation(s) | Ontario Institute for Cancer Research, University of Toronto |
| Primary contact | Email: Paul dot Boutros at oicr dot on dot ca |
| Year published | 2016 |
| Volume and issue | 17 |
| Page(s) | 401 |
| DOI | 10.1186/s12859-016-1281-5 |
| ISSN | 1471-2105 |
| Distribution license | Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International |
| Website | http://bmcbioinformatics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12859-016-1281-5 |
| Download | http://bmcbioinformatics.biomedcentral.com/track/pdf/10.1186/s12859-016-1281-5 (PDF) |
|
|
This article should not be considered complete until this message box has been removed. This is a work in progress. |
Abstract
Background
Visualization of data generated by high-throughput, high-dimensionality experiments is rapidly becoming a rate-limiting step in computational biology. There is an ongoing need to quickly develop high-quality visualizations that can be easily customized or incorporated into automated pipelines. This often requires an interface for manual plot modification, rapid cycles of tweaking visualization parameters, and the generation of graphics code. To facilitate this process for the generation of highly-customizable, high-resolution Venn and Euler diagrams, we introduce VennDiagramWeb: a web application for the widely used VennDiagram R package. VennDiagramWeb is hosted at http://venndiagram.res.oicr.on.ca/.
Results
VennDiagramWeb allows real-time modification of Venn and Euler diagrams, with parameter setting through a web interface and immediate visualization of results. It allows customization of essentially all aspects of figures, but also supports integration into computational pipelines via download of R code. Users can upload data and download figures in a range of formats, and there is exhaustive support documentation.
Conclusions
VennDiagramWeb allows the easy creation of Venn and Euler diagrams for computational biologists, and indeed many other fields. Its ability to support real-time graphics changes that are linked to downloadable code that can be integrated into automated pipelines will greatly facilitate the improved visualization of complex datasets. For application support please contact PPaul dot Boutros at oicr dot on dot ca.
Background
Data visualization is a growing and important area of computational biology that demands high quality images which highlight the critical aspects of data. To elucidate all essential features of the data, one must perform a wide range of adjustments to various aspects of the plot, which can be a time-consuming process. Having fine-grained control over the parameters which define colors, fonts, label placements, element sizes, overall resolution, etc. leads to more effective plots which can convey necessary details in a publication-ready manner.
Pipelines facilitate automated, robust and reproducible data generation and analysis. Plotting is an important tool for both validation and reporting of results. Incorporating effective plots into these pipelines requires code that has been written specifically for each plot, as there is no single approach which can be applied to varied datasets. As a result, bioinformaticians often engage in long cycles of sequentially modifying plotting code, executing it, and observing the ultimate figure, until an optimum is reached. This process is inefficient and time-consuming.
Venn and Euler diagrams are used frequently in computational biology to visualize the interactions between multiple sets of data. In genomics especially, a common assay is to compare gene lists occurring from separate analyses[1], such as contrasting lists of differentially abundant RNAs following drug treatments or lists of mutated genes across disease types. Venn diagrams are typically depicted as partially intersecting circles or other closed curves such that there are 2n separated regions as depicted by overlapping closed curves.[2] While Venn diagrams always depict all 2n possible regions, Euler diagrams can omit regions under which there are zero values in that region’s subset. This allows Euler diagrams to be less visually complex, by depicting only a subset of all possible regions.[3] VennDiagramWeb facilitates the creation of both Venn and Euler diagrams, using the argument euler.d and scaled (both default TRUE). By default, VennDiagramWeb will create an Euler diagram where possible, displaying only regions containing one or more values. Users can force Venn diagrams only by setting both euler.d = FALSE and scaled = FALSE (Fig. 1).
|
The R statistical programming language has widespread use in the bioinformatics field, and so we developed VennDiagram to generate plots in this language.[4] The initial release has proven to be robust and useful, and has garnered 186 citations. As of June 8, 2016 the package has been downloaded from the Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN) over 75,000 times since its release in March 2011. Over half of these (>40,000) occurred in 2015 alone, highlighting growing popularity.[5]
References
- ↑ Bardou, P.; Mariette, J.; Escudié, F. et al. (2014). "jvenn: An interactive Venn diagram viewer". BMC Bioinformatics 15: 293. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-15-293. PMC PMC4261873. PMID 25176396. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4261873.
- ↑ "Venn Diagram". MathWorld. Wolfram Research, Inc. http://mathworld.wolfram.com/VennDiagram.html. Retrieved 22 August 2016.
- ↑ Rodger, P. (22 September 2004). "Venn Diagrams, Euler Diagrams and Leibniz". Euler Diagrams 2004. https://www.cs.kent.ac.uk/events/conf/2004/euler/eulerdiagrams.html. Retrieved 22 August 2016.
- ↑ Chen, H.; Boutros, P.C. (2011). "VennDiagram: A package for the generation of highly-customizable Venn and Euler diagrams in R". BMC Bioinformatics 12: 35. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-12-35. PMC PMC3041657. PMID 21269502. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3041657.
- ↑ "cranlogs: Download Logs from the RStudio CRAN Mirror". GitHub. GitHub, Inc. https://github.com/metacran/cranlogs. Retrieved 08 June 2016.
Notes
This presentation is faithful to the original, with only a few minor changes to presentation. In some cases important information was missing from the references, and that information was added.