Difference between revisions of "Redmine"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated language.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) m (Added cat.) |
||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
[[Category:Bug tracking software (open source)]] | [[Category:Bug tracking software (open source)]] | ||
[[Category:Project management software (open source)]] | [[Category:Project management software (open source)]] | ||
[[Category:Software development tool (open source)]] | |||
[[Category:Ticket tracking software (open source)]] | [[Category:Ticket tracking software (open source)]] | ||
Revision as of 18:44, 23 March 2012
|
| |
| Developer(s) | Jean-Philippe Lang |
|---|---|
| Initial release | June 25, 2006[1] |
| Stable release |
5.1.2 and 5.0.8 (March 4, 2024) [±] |
| Preview release | none [±] |
| Written in | Ruby, Ruby on Rails |
| Operating system | Cross-platform |
| Type |
Project management software Bug tracking software |
| License(s) | GNU General Public License v2 |
| Website | www.redmine.org |
Redmine is flexible web-based project management software that's based on a Ruby on Rails framework. The design of Redmine is significantly influenced by Trac, a software package with similar features.
Product history
Redmine was introduced on RubyForge with version 0.1.0 on June 25, 2006.[1]
Features
Main features of Redmine include[2]:
- multiple project and subproject support
- role-based security
- bug tracking system
- Gantt charts and calendars
- project- and work-based time tracking
- custom fields and interface
- document management
- project-based wikis
- SCM integration (Subversion, CVS, Mercurial, Darcs, Bazaar, and Git)
- web feeds and e-mail support
- lightweight directory access protocol (LDAP) support
- multi-language support
Hardware/software requirements
Requirements for this software to run properly include[3]:
1. MySQL 5.0 or higher, PostgreSQL 8, or SQLite 3
2. an appropriate version of Ruby and Ruby on Rails (see below)
The version of Ruby and Ruby on Rails necessary for proper software function depends on which version of Redmine you wish to install. Reference Redmine's install requirements for those dependencies and other dependencies for SQL databases, etc. here.
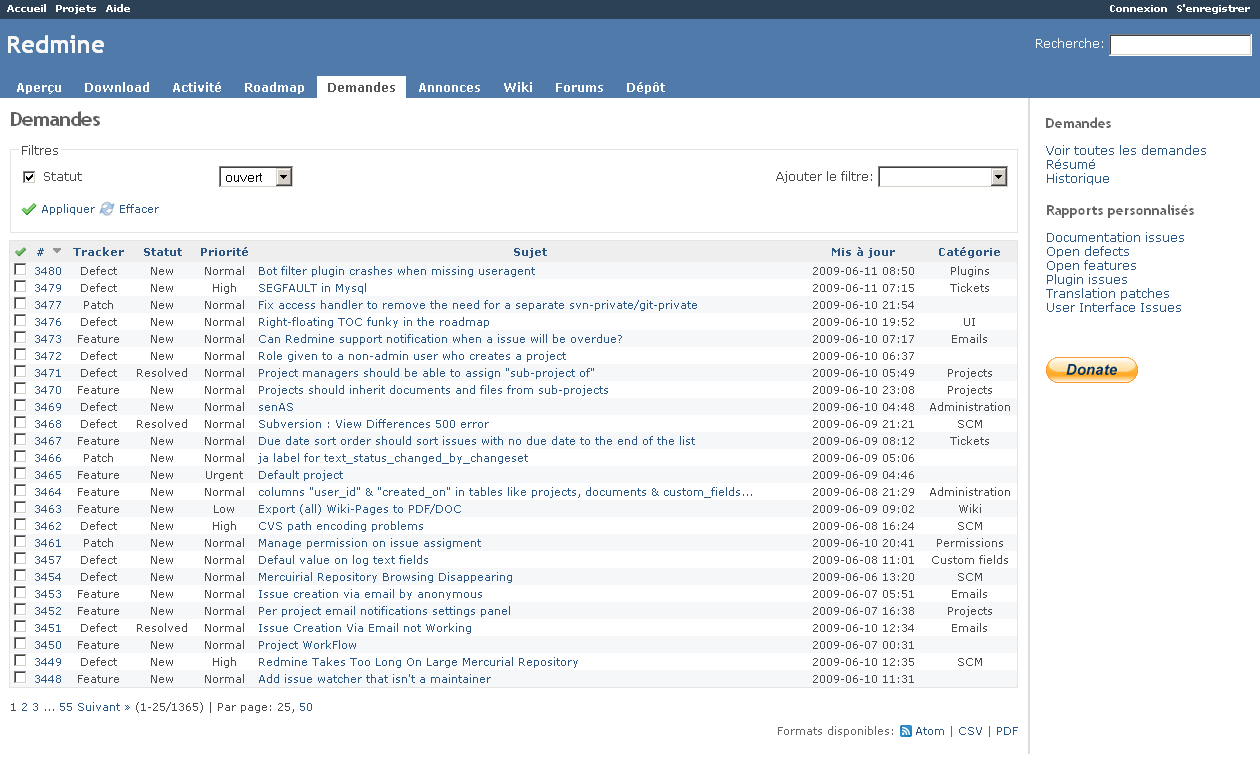
Videos, screenshots, and other media
Click a screenshot to see a larger version. Alternatively, right-click and choose to open it in a separate tab/window.
Online video tutorials of Redmine can be found here.
An online demo of Redmine can be found on the project's demo site.
Entities using Redmine
Examples of entities that use Redmine include:
BioRails, Institute for Climate and Atmospheric Science at University of Leeds, Institut Supérieur de l'Aéronautique et de l'Espace, Laboratoire de recherche informatique LIM, Michigan State University Hydrogeology Lab, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, SRH Hochschule Heidelberg, Thiagarajar College of Engineering, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute Genome Campus
A full directory of Redmine users can be found at the Redmine website.
Further reading
- "Redmine user and developer guides". Jean-Philippe Lang. http://www.redmine.org/projects/redmine/wiki/Guide.
- "Redmine integration with Subversion and other SCM tools". Jean-Philippe Lang. http://www.redmine.org/projects/redmine/wiki/RedmineRepositories.
External links
- Redmine project page on RubyForge
- RedmineApp, an iPhone app for Redmine
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "RubyForge: Redmine: Project Filelist". RubyForge.org. http://rubyforge.org/frs/?group_id=1850. Retrieved 14 March 2012.
- ↑ "Features - Redmine". Jean-Philippe Lang. http://www.redmine.org/projects/redmine/wiki/Features. Retrieved 9 March 2012.
- ↑ "Installing Redmine". Jean-Philippe Lang. http://www.redmine.org/projects/redmine/wiki/RedmineInstall. Retrieved 14 March 2012.