Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig2 Jadhav IntJofMolSci23 24-9.png|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:A metabolomics and big data approach to cannabis authenticity (authentomics)|A metabolomics and big data approach to cannabis authenticity (authentomics)]]"''' | ||
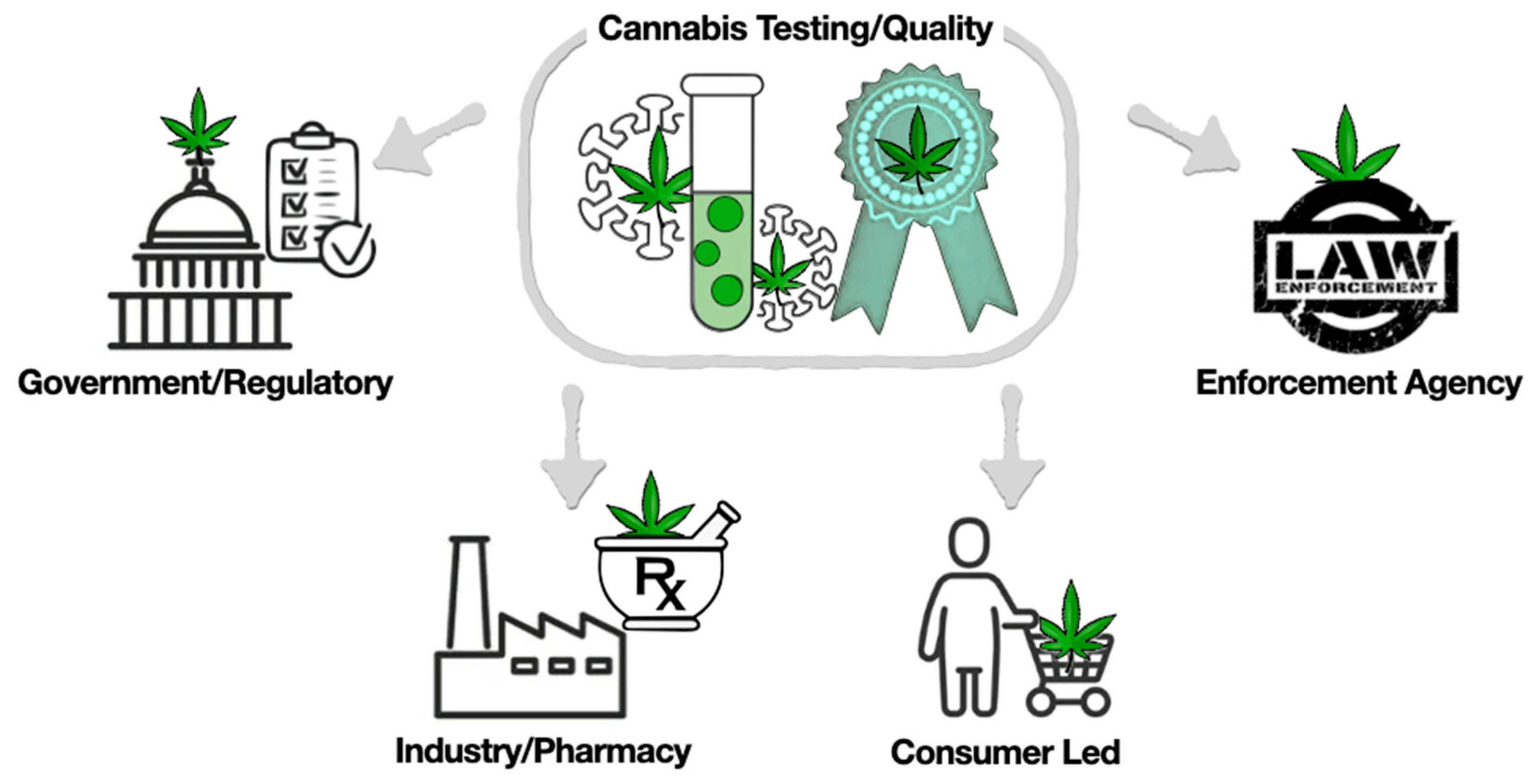
With the | With the increasing accessibility of [[cannabis]] ([[Cannabis sativa|''Cannabis sativa'' L.]], also known as marijuana and [[hemp]]), its products are being developed as [[Cannabis concentrate|extracts]] for both recreational and [[Cannabis (drug)|therapeutic]] use. This has led to increased scrutiny by [[Regulatory compliance|regulatory bodies]], who aim to understand and regulate the complex chemistry of these products to ensure their safety and efficacy. Regulators use targeted analyses to track the concentration of key bioactive [[Metabolomics|metabolites]] and potentially harmful [[Contamination|contaminants]], such as [[heavy metals]] and other impurities. However, the complexity of cannabis' metabolic pathways requires a more comprehensive approach. A non-targeted metabolomic analysis of cannabis products is necessary to generate data that can be used to determine their authenticity and efficacy ... ('''[[Journal:A metabolomics and big data approach to cannabis authenticity (authentomics)|Full article...]]''')<br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
{{flowlist | | {{flowlist | | ||
* [[Journal:Integration of X-ray absorption fine structure databases for data-driven materials science|Integration of X-ray absorption fine structure databases for data-driven materials science]] | |||
* [[Journal:Management and disclosure of quality issues in forensic science: A survey of current practice in Australia and New Zealand|Management and disclosure of quality issues in forensic science: A survey of current practice in Australia and New Zealand]] | * [[Journal:Management and disclosure of quality issues in forensic science: A survey of current practice in Australia and New Zealand|Management and disclosure of quality issues in forensic science: A survey of current practice in Australia and New Zealand]] | ||
* [[Journal:Thirty years of the DICOM standard|Thirty years of the DICOM standard]] | * [[Journal:Thirty years of the DICOM standard|Thirty years of the DICOM standard]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 19:47, 16 January 2024
"A metabolomics and big data approach to cannabis authenticity (authentomics)"
With the increasing accessibility of cannabis (Cannabis sativa L., also known as marijuana and hemp), its products are being developed as extracts for both recreational and therapeutic use. This has led to increased scrutiny by regulatory bodies, who aim to understand and regulate the complex chemistry of these products to ensure their safety and efficacy. Regulators use targeted analyses to track the concentration of key bioactive metabolites and potentially harmful contaminants, such as heavy metals and other impurities. However, the complexity of cannabis' metabolic pathways requires a more comprehensive approach. A non-targeted metabolomic analysis of cannabis products is necessary to generate data that can be used to determine their authenticity and efficacy ... (Full article...)
Recently featured: