Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Scheibner BMCMedEthics22 23.png|240px]]</div> | ||
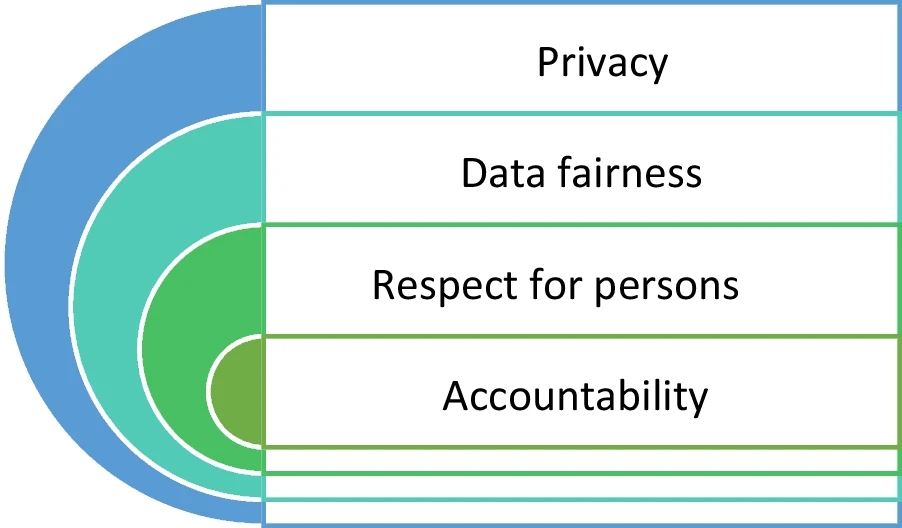
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Health data privacy through homomorphic encryption and distributed ledger computing: An ethical-legal qualitative expert assessment study|Health data privacy through homomorphic encryption and distributed ledger computing: An ethical-legal qualitative expert assessment study]]"''' | ||
Increasingly, [[hospital]]s and research institutes are developing technical solutions for [[Data sharing|sharing patient data]] in a [[Information privacy|privacy-preserving manner]]. Two of these technical solutions are [[homomorphic encryption]] and [[Blockchain|distributed ledger]] technology. Homomorphic encryption allows computations to be performed on data without this data ever being decrypted. Therefore, homomorphic encryption represents a potential solution for conducting feasibility studies on cohorts of sensitive patient data stored in distributed locations. Distributed ledger technology provides a permanent record on all transfers and processing of patient data, allowing data custodians to audit access. A significant portion of the current literature has examined how these technologies might comply with data protection and research ethics frameworks ... ('''[[Journal:Health data privacy through homomorphic encryption and distributed ledger computing: An ethical-legal qualitative expert assessment study|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
{{flowlist | | {{flowlist | | ||
* [[Journal:Avoidance of operational sampling errors in drinking water analysis|Avoidance of operational sampling errors in drinking water analysis]] | |||
* [[Journal:ISO/IEC 17025: History and introduction of concepts|ISO/IEC 17025: History and introduction of concepts]] | * [[Journal:ISO/IEC 17025: History and introduction of concepts|ISO/IEC 17025: History and introduction of concepts]] | ||
* [[Journal:Practical considerations for laboratories: Implementing a holistic quality management system|Practical considerations for laboratories: Implementing a holistic quality management system]] | * [[Journal:Practical considerations for laboratories: Implementing a holistic quality management system|Practical considerations for laboratories: Implementing a holistic quality management system]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 18:03, 19 June 2023
Increasingly, hospitals and research institutes are developing technical solutions for sharing patient data in a privacy-preserving manner. Two of these technical solutions are homomorphic encryption and distributed ledger technology. Homomorphic encryption allows computations to be performed on data without this data ever being decrypted. Therefore, homomorphic encryption represents a potential solution for conducting feasibility studies on cohorts of sensitive patient data stored in distributed locations. Distributed ledger technology provides a permanent record on all transfers and processing of patient data, allowing data custodians to audit access. A significant portion of the current literature has examined how these technologies might comply with data protection and research ethics frameworks ... (Full article...)
Recently featured: