Difference between revisions of "Main Page/Featured article of the week/2023"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Added last week's article of the week) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Added last week's article of the week) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
<!-- Below this line begin pasting previous news --> | <!-- Below this line begin pasting previous news --> | ||
<h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: January 09–15:</h2> | <h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: January 16–22:</h2> | ||
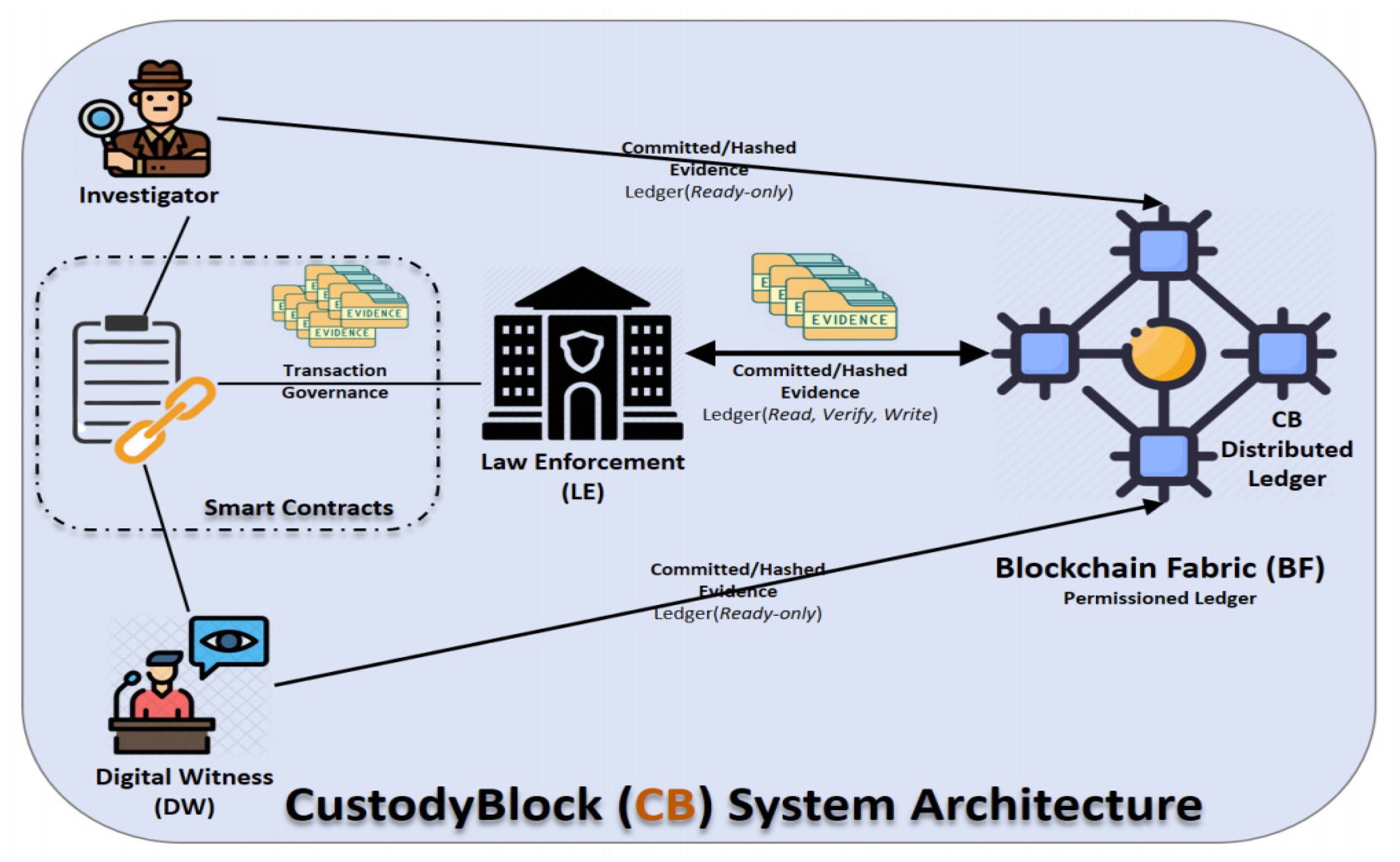
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig3 Alruwaili Information21 12-2.png|240px]]</div> | |||
'''"[[Journal:CustodyBlock: A distributed chain of custody evidence framework|CustodyBlock: A distributed chain of custody evidence framework]]"''' | |||
With the increasing number of cybercrimes, the [[digital forensics]] team has no choice but to implement more robust and resilient evidence-handling mechanisms. The capturing of digital evidence, which is a tangible and probative piece of [[information]] that can be presented in court and used in trial, is challenging due to its volatility and the possible effects of improper handling procedures. When computer systems get compromised, digital forensics comes into play to analyze, discover, extract, and preserve all relevant evidence. Therefore, it is imperative to maintain efficient [[wikipedia:Evidence management|evidence management]] to guarantee the credibility and admissibility of digital evidence in a court of law. A critical component of this process is to utilize an adequate [[chain of custody]] (CoC) approach to preserve the evidence in its original state from compromise and/or contamination ... ('''[[Journal:CustodyBlock: A distributed chain of custody evidence framework|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: January 09–15:</h2> | |||
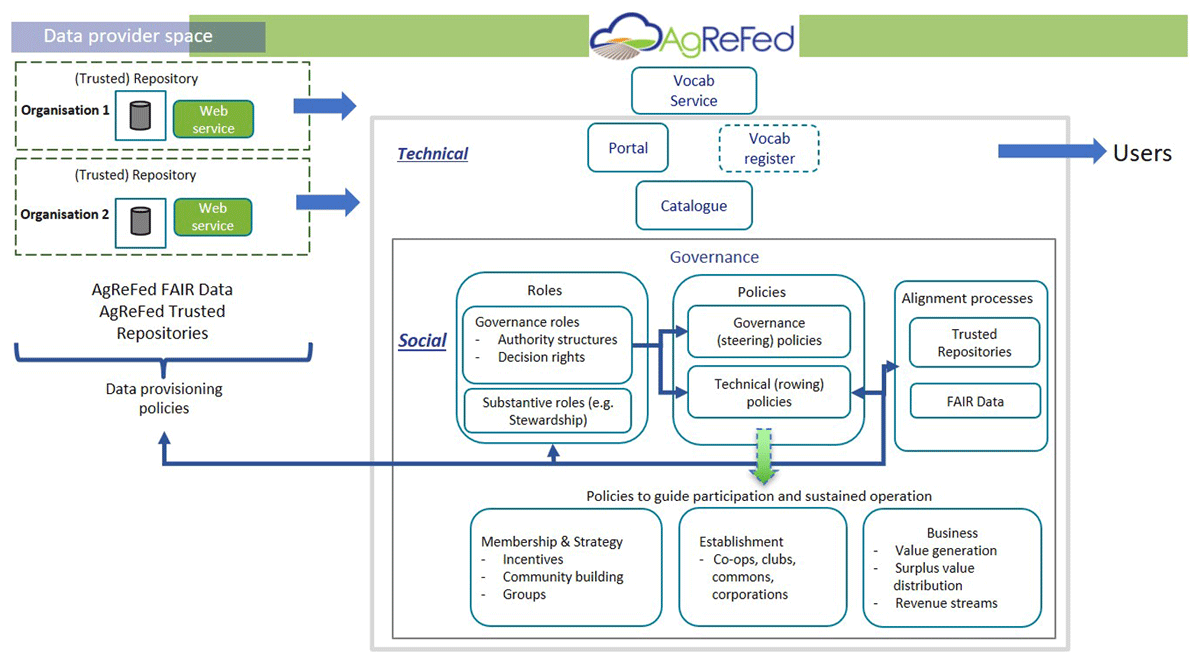
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Wong DataSciJourn22 21-1.png|240px]]</div> | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Wong DataSciJourn22 21-1.png|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal:Development and governance of FAIR thresholds for a data federation|Development and governance of FAIR thresholds for a data federation]]"''' | '''"[[Journal:Development and governance of FAIR thresholds for a data federation|Development and governance of FAIR thresholds for a data federation]]"''' | ||
Revision as of 17:16, 23 January 2023
|
|
If you're looking for other "Article of the Week" archives: 2014 - 2015 - 2016 - 2017 - 2018 - 2019 - 2020 - 2021 - 2022 - 2023 |
Featured article of the week archive - 2023
Welcome to the LIMSwiki 2023 archive for the Featured Article of the Week.
Featured article of the week: January 16–22:"CustodyBlock: A distributed chain of custody evidence framework" With the increasing number of cybercrimes, the digital forensics team has no choice but to implement more robust and resilient evidence-handling mechanisms. The capturing of digital evidence, which is a tangible and probative piece of information that can be presented in court and used in trial, is challenging due to its volatility and the possible effects of improper handling procedures. When computer systems get compromised, digital forensics comes into play to analyze, discover, extract, and preserve all relevant evidence. Therefore, it is imperative to maintain efficient evidence management to guarantee the credibility and admissibility of digital evidence in a court of law. A critical component of this process is to utilize an adequate chain of custody (CoC) approach to preserve the evidence in its original state from compromise and/or contamination ... (Full article...)
|