Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) m (Fix) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig2 Krupitzer Foods21 10-11.png|240px]]</div> | ||
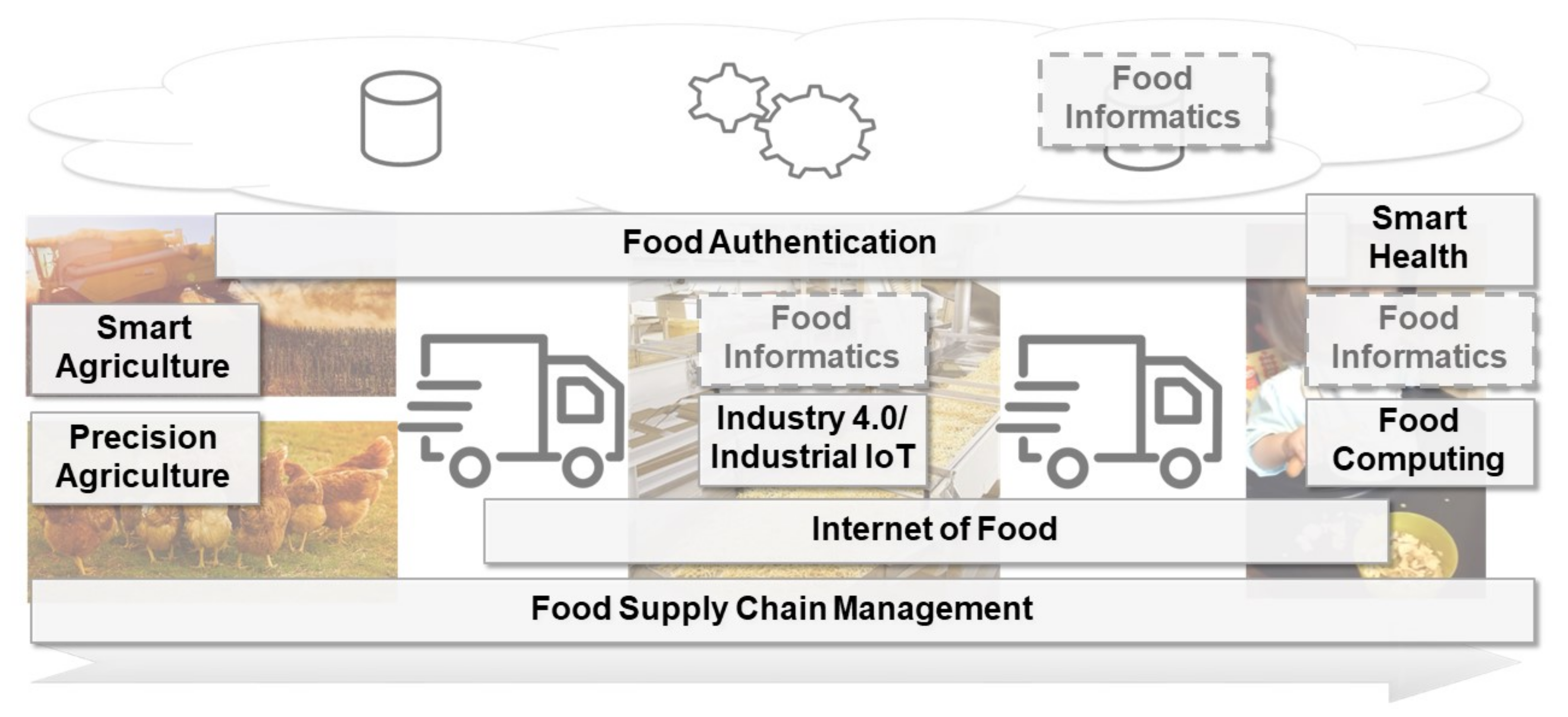
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Food informatics: Review of the current state-of-the-art, revised definition, and classification into the research landscape|Food informatics: Review of the current state-of-the-art, revised definition, and classification into the research landscape]]"''' | ||
The | The increasing population of humans and their changing food consumption behavior, as well as the recent developments in the awareness for food sustainability, lead to new challenges for the production of food. Advances in the [[internet of things]] (IoT) and [[artificial intelligence]] (AI) technology, including [[machine learning]] and [[Data analysis|data analytics]], might help to account for these challenges. Several research perspectives—among them precision agriculture, industrial IoT, internet of food, and smart health—already provide new opportunities through digitalization. In this paper, we review the current state-of-the-art of the mentioned concepts. An additional concept to address is food informatics, which so far is mostly recognized as a mainly data-driven approach to support the production of food. In this review paper, we propose and discuss a new perspective for the concept of food informatics as a supportive discipline ... ('''[[Journal:Food informatics: Review of the current state-of-the-art, revised definition, and classification into the research landscape|Full article...]]''')<br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
{{flowlist | | {{flowlist | | ||
* [[Journal:Creating learning health systems and the emerging role of biomedical informatics|Creating learning health systems and the emerging role of biomedical informatics]] | |||
* [[LII:Planning for Disruptions in Laboratory Operations|Planning for Disruptions in Laboratory Operations]] | * [[LII:Planning for Disruptions in Laboratory Operations|Planning for Disruptions in Laboratory Operations]] | ||
* [[Journal:The current state of knowledge on imaging informatics: A survey among Spanish radiologists|The current state of knowledge on imaging informatics: A survey among Spanish radiologists]] | * [[Journal:The current state of knowledge on imaging informatics: A survey among Spanish radiologists|The current state of knowledge on imaging informatics: A survey among Spanish radiologists]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 14:59, 24 October 2022
The increasing population of humans and their changing food consumption behavior, as well as the recent developments in the awareness for food sustainability, lead to new challenges for the production of food. Advances in the internet of things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) technology, including machine learning and data analytics, might help to account for these challenges. Several research perspectives—among them precision agriculture, industrial IoT, internet of food, and smart health—already provide new opportunities through digitalization. In this paper, we review the current state-of-the-art of the mentioned concepts. An additional concept to address is food informatics, which so far is mostly recognized as a mainly data-driven approach to support the production of food. In this review paper, we propose and discuss a new perspective for the concept of food informatics as a supportive discipline ... (Full article...)
Recently featured: