Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
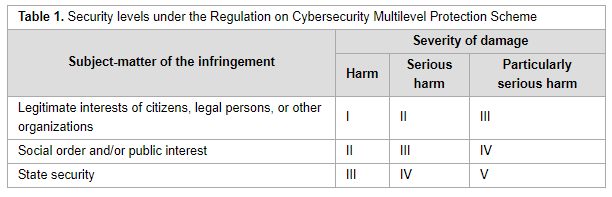
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Tab1 Li RivItal21 3-1.png|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Cross-border data transfer regulation in China|Cross-border data transfer regulation in China]]"''' | ||
With the growing participation of emerging countries in global data governance, the traditional legislative paradigm dominated by the European Union and the United States is constantly being analyzed and reshaped. It is of particular importance for China to establish the regulatory framework of cross-border data transfer, for not only does it involve the rights of Chinese citizens and entities, but also the concepts of cyber-sovereignty and national security, as well as the framing of global cyberspace rules. China continues to leverage data sovereignty to persuade lawmakers to support the development of critical technology in digital domains and infrastructure construction. This paper aims to systematically and chronologically describe Chinese regulations for cross-border data exchange. Enacted and draft provisions—as well as binding and non-binding regulatory rules—are studied, and various positive dynamic developments in the framing of China’s cross-border data regulation are shown ... ('''[[Journal:Cross-border data transfer regulation in China|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
{{flowlist | | {{flowlist | | ||
* [[Journal:Data and information systems management for urban water infrastructure condition assessment|Data and information systems management for urban water infrastructure condition assessment]] | |||
* [[Journal:Diagnostic informatics: The role of digital health in diagnostic stewardship and the achievement of excellence, safety, and value|Diagnostic informatics: The role of digital health in diagnostic stewardship and the achievement of excellence, safety, and value]] | * [[Journal:Diagnostic informatics: The role of digital health in diagnostic stewardship and the achievement of excellence, safety, and value|Diagnostic informatics: The role of digital health in diagnostic stewardship and the achievement of excellence, safety, and value]] | ||
* [[Journal:Development and implementation of an LIS-based validation system for autoverification toward zero defects in the automated reporting of laboratory test results|Development and implementation of an LIS-based validation system for autoverification toward zero defects in the automated reporting of laboratory test results]] | * [[Journal:Development and implementation of an LIS-based validation system for autoverification toward zero defects in the automated reporting of laboratory test results|Development and implementation of an LIS-based validation system for autoverification toward zero defects in the automated reporting of laboratory test results]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 15:10, 18 April 2022
"Cross-border data transfer regulation in China"
With the growing participation of emerging countries in global data governance, the traditional legislative paradigm dominated by the European Union and the United States is constantly being analyzed and reshaped. It is of particular importance for China to establish the regulatory framework of cross-border data transfer, for not only does it involve the rights of Chinese citizens and entities, but also the concepts of cyber-sovereignty and national security, as well as the framing of global cyberspace rules. China continues to leverage data sovereignty to persuade lawmakers to support the development of critical technology in digital domains and infrastructure construction. This paper aims to systematically and chronologically describe Chinese regulations for cross-border data exchange. Enacted and draft provisions—as well as binding and non-binding regulatory rules—are studied, and various positive dynamic developments in the framing of China’s cross-border data regulation are shown ... (Full article...)
Recently featured:
- Data and information systems management for urban water infrastructure condition assessment
- Diagnostic informatics: The role of digital health in diagnostic stewardship and the achievement of excellence, safety, and value
- Development and implementation of an LIS-based validation system for autoverification toward zero defects in the automated reporting of laboratory test results