Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig2 Seifert JAMIAOpen20 3.png|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Informatics-driven quality improvement in the modern histology lab|Informatics-driven quality improvement in the modern histology lab]]"''' | ||
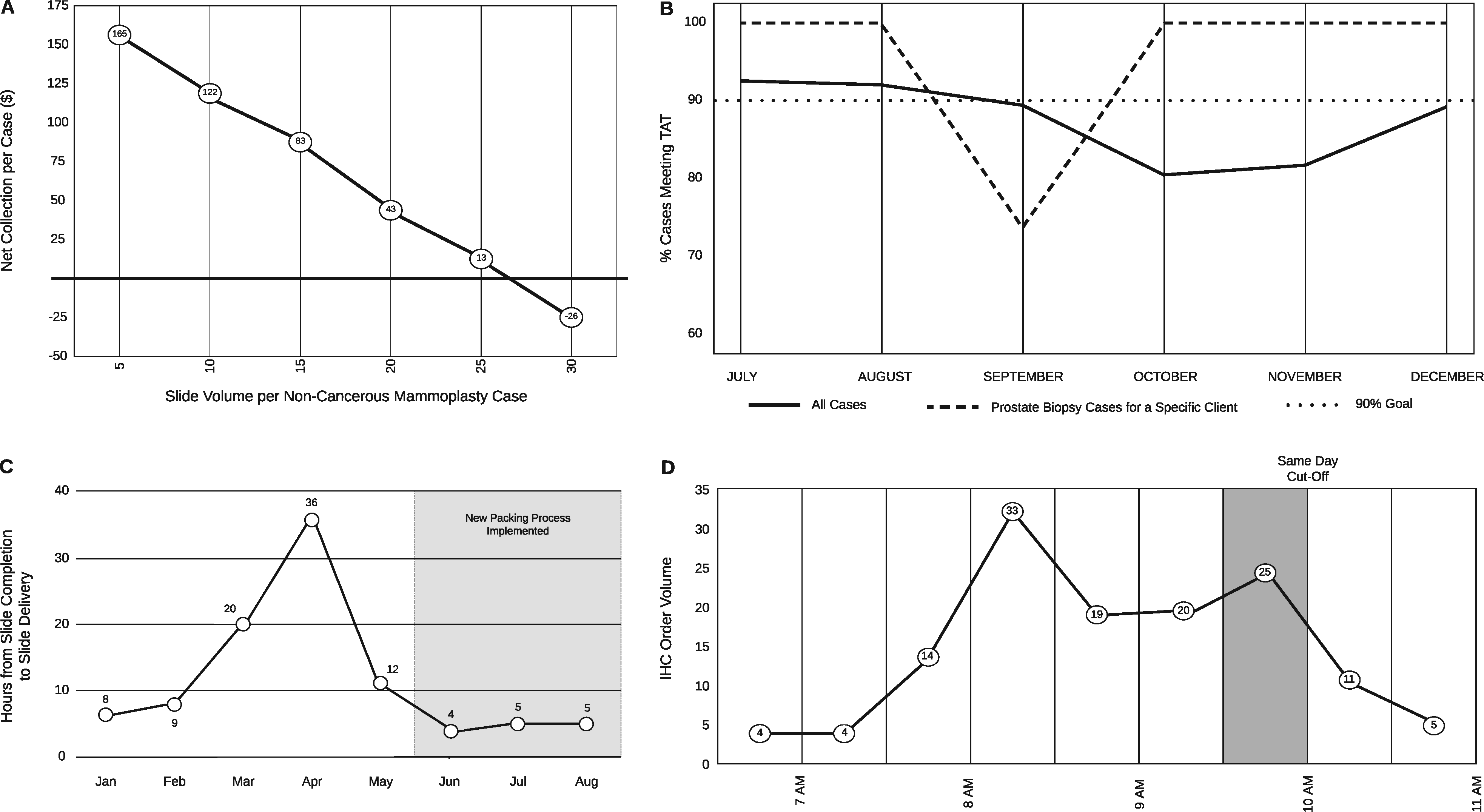
[[Laboratory information system]]s (LISs) and [[data visualization]] techniques have untapped potential in [[Anatomical pathology|anatomic pathology]] [[Laboratory|laboratories]]. The pre-built functionalities of an LIS do not address all the needs of a modern [[histology]] laboratory. For instance, “go live” is not the end of LIS customization, only the beginning. After closely evaluating various histology lab [[workflows]], we implemented several custom [[Data analysis|data analytics]] dashboards and additional LIS functionalities to monitor and address weaknesses. Herein, we present our experience with LIS and data-tracking solutions that improved trainee education, slide logistics, staffing and instrumentation lobbying, and task tracking. The latter was addressed through the creation of a novel “status board” akin to those seen in inpatient wards. These use-cases can benefit other histology laboratories. ('''[[Journal:Informatics-driven quality improvement in the modern histology lab|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
{{flowlist | | {{flowlist | | ||
* [[Journal:Popularity and performance of bioinformatics software: The case of gene set analysis|Popularity and performance of bioinformatics software: The case of gene set analysis]] | |||
* [[Journal:Privacy-preserving healthcare informatics: A review|Privacy-preserving healthcare informatics: A review]] | * [[Journal:Privacy-preserving healthcare informatics: A review|Privacy-preserving healthcare informatics: A review]] | ||
* [[Journal:Secure data outsourcing in presence of the inference problem: Issues and directions|Secure data outsourcing in presence of the inference problem: Issues and directions]] | * [[Journal:Secure data outsourcing in presence of the inference problem: Issues and directions|Secure data outsourcing in presence of the inference problem: Issues and directions]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 17:41, 14 February 2022
"Informatics-driven quality improvement in the modern histology lab"
Laboratory information systems (LISs) and data visualization techniques have untapped potential in anatomic pathology laboratories. The pre-built functionalities of an LIS do not address all the needs of a modern histology laboratory. For instance, “go live” is not the end of LIS customization, only the beginning. After closely evaluating various histology lab workflows, we implemented several custom data analytics dashboards and additional LIS functionalities to monitor and address weaknesses. Herein, we present our experience with LIS and data-tracking solutions that improved trainee education, slide logistics, staffing and instrumentation lobbying, and task tracking. The latter was addressed through the creation of a novel “status board” akin to those seen in inpatient wards. These use-cases can benefit other histology laboratories. (Full article...)
Recently featured: