Difference between revisions of "File:Fig1 Tsai JofPersMed2016 6-1.png"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Added summary.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Summary== | |||
{{Information | |||
|Description='''Figure 1.''' WGS Alignment and Variant Calling Pipeline. There are multiple entry points to our pipeline where it can be re-triggered due to system failures or outside datasets. Standard processing of genome data from the Illumina Clinical Services Laboratory starts at the top entry point. From there, FASTQ sequences are aligned to the reference hg19 genome using the burrows-wheeler aligner (bwa). Since the alignment is computationally intensive, we divided the sequence files into smaller files. The alignments, known as “raw” BAM files in our pipeline, are processed through a series of steps prior to variant calling. The “final” BAM file is the resulting file after removing PCR artifacts, local indel realignment, and base quality recalibration. This is used as the input file to the variant caller portion of the pipeline. Variant calling happens in two phases, where the variants are identified and then their quality scores are recalibrated in the final VCF file. | |||
|Source={{cite journal |journal=Journal of Personalized Medicine |title=Bioinformatics workflow for clinical whole genome sequencing at Partners HealthCare Personalized Medicine |author=Tsai, E.A.; Shakbatyan, R.; Evan, J.; Rossetti, P.; Graham, C.; Sharma, H.; Lin, C.-F., Lebo, M.S. |volume=6 |issue=1 |pages=12 |year=2016 |doi=10.3390/jpm6010012 |pmid=26927186 |pmc=PMC4810391}} | |||
|Author=Tsai, E.A.; Shakbatyan, R.; Evan, J.; Rossetti, P.; Graham, C.; Sharma, H.; Lin, C.-F., Lebo, M.S. | |||
|Date=2016 | |||
|Permission=[http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International] | |||
}} | |||
== Licensing == | == Licensing == | ||
{{cc-by-4.0}} | {{cc-by-4.0}} | ||
Latest revision as of 21:21, 21 November 2016
Summary
| Description |
Figure 1. WGS Alignment and Variant Calling Pipeline. There are multiple entry points to our pipeline where it can be re-triggered due to system failures or outside datasets. Standard processing of genome data from the Illumina Clinical Services Laboratory starts at the top entry point. From there, FASTQ sequences are aligned to the reference hg19 genome using the burrows-wheeler aligner (bwa). Since the alignment is computationally intensive, we divided the sequence files into smaller files. The alignments, known as “raw” BAM files in our pipeline, are processed through a series of steps prior to variant calling. The “final” BAM file is the resulting file after removing PCR artifacts, local indel realignment, and base quality recalibration. This is used as the input file to the variant caller portion of the pipeline. Variant calling happens in two phases, where the variants are identified and then their quality scores are recalibrated in the final VCF file. |
|---|---|
| Source |
Tsai, E.A.; Shakbatyan, R.; Evan, J.; Rossetti, P.; Graham, C.; Sharma, H.; Lin, C.-F., Lebo, M.S. (2016). "Bioinformatics workflow for clinical whole genome sequencing at Partners HealthCare Personalized Medicine". Journal of Personalized Medicine 6 (1): 12. doi:10.3390/jpm6010012. PMC PMC4810391. PMID 26927186. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4810391. |
| Date |
2016 |
| Author |
Tsai, E.A.; Shakbatyan, R.; Evan, J.; Rossetti, P.; Graham, C.; Sharma, H.; Lin, C.-F., Lebo, M.S. |
| Permission (Reusing this file) |
|
| Other versions |
Licensing
|
|
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License. |
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 21:17, 21 November 2016 | 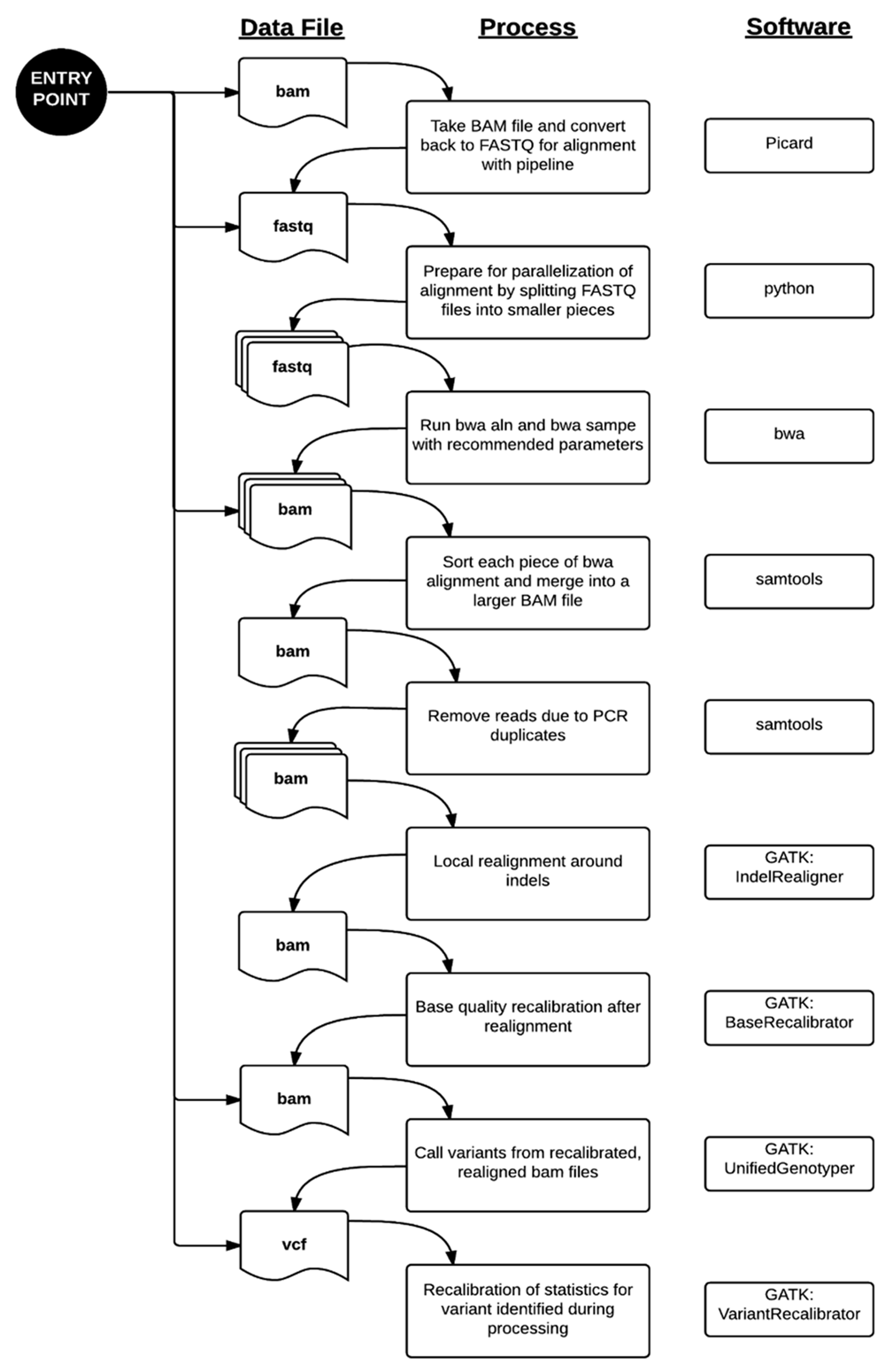 | 1,000 × 1,550 (113 KB) | Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file:









