Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
||
| (29 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Signoroni NatComm23 14.png|240px]]</div> | ||
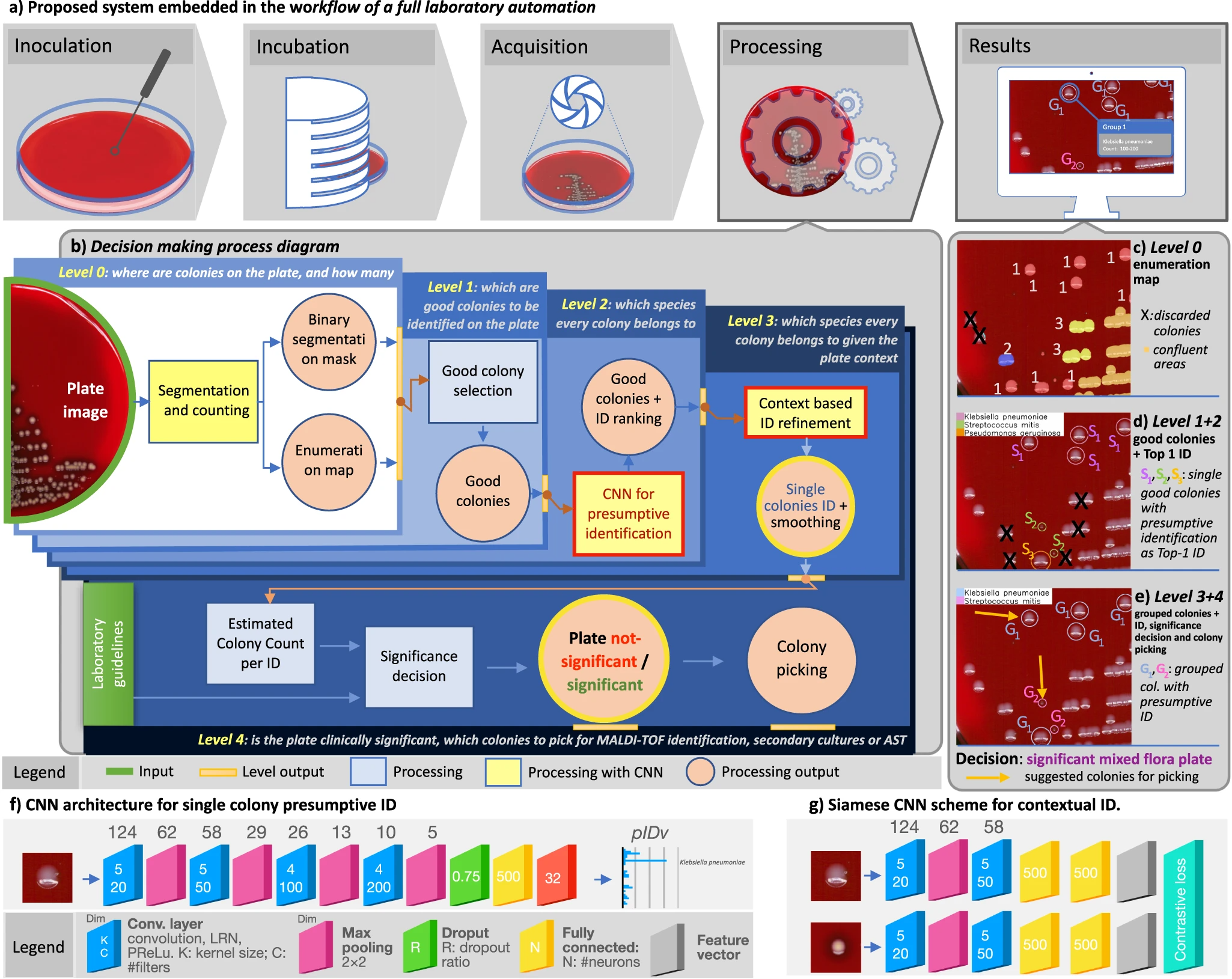
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Hierarchical AI enables global interpretation of culture plates in the era of digital microbiology|Hierarchical AI enables global interpretation of culture plates in the era of digital microbiology]]"''' | ||
[[ | Full [[laboratory automation]] is revolutionizing work habits in an increasing number of clinical [[microbiology]] facilities worldwide, generating huge streams of [[Imaging|digital images]] for interpretation. Contextually, [[deep learning]] (DL) architectures are leading to paradigm shifts in the way computers can assist with difficult visual interpretation tasks in several domains. At the crossroads of these epochal trends, we present a system able to tackle a core task in clinical microbiology, namely the global interpretation of diagnostic [[Bacteria|bacterial]] [[Cell culture|culture]] plates, including presumptive [[pathogen]] identification. This is achieved by decomposing the problem into a hierarchy of complex subtasks and addressing them with a multi-network architecture we call DeepColony ... ('''[[Journal:Hierarchical AI enables global interpretation of culture plates in the era of digital microbiology|Full article...]]''')<br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
{{flowlist | | {{flowlist | | ||
* [[Journal: | * [[Journal:Critical analysis of the impact of AI on the patient–physician relationship: A multi-stakeholder qualitative study|Critical analysis of the impact of AI on the patient–physician relationship: A multi-stakeholder qualitative study]] | ||
* [[Journal: | * [[Journal:Judgements of research co-created by generative AI: Experimental evidence|Judgements of research co-created by generative AI: Experimental evidence]] | ||
* [[Journal: | * [[Journal:Geochemical biodegraded oil classification using a machine learning approach|Geochemical biodegraded oil classification using a machine learning approach]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 15:02, 3 June 2024
"Hierarchical AI enables global interpretation of culture plates in the era of digital microbiology"
Full laboratory automation is revolutionizing work habits in an increasing number of clinical microbiology facilities worldwide, generating huge streams of digital images for interpretation. Contextually, deep learning (DL) architectures are leading to paradigm shifts in the way computers can assist with difficult visual interpretation tasks in several domains. At the crossroads of these epochal trends, we present a system able to tackle a core task in clinical microbiology, namely the global interpretation of diagnostic bacterial culture plates, including presumptive pathogen identification. This is achieved by decomposing the problem into a hierarchy of complex subtasks and addressing them with a multi-network architecture we call DeepColony ... (Full article...)
Recently featured: